
They say beauty is only skin deep, but true beauty starts at the cellular level, far below the skin’s surface. Every year, consumers spend billions of dollars on skincare products in hopes of achieving more beautiful skin. According to industry forecasts from sources like Statista and Grand View Research, the US skincare and beauty market is projected to reach $25 billion in 2025. But even the very best skin care products only render temporary results. For beautiful skin that starts from within, you need to provide your body with high-quality nutrients that support the formation and function of new skin cells.
Learn how glutathione, a powerful antioxidant nutrient, is helping thousands to lighten, tighten and brighten their skin while diminishing the appearance of freckles, age spots and uneven pigmentation.
Building Healthy Skin from Within
About 90% of the cells of your epidermis – the outermost layer of skin – are keratinocytes. They are formed through a process called keratinization, aka epidermal cell differentiation. The process begins in the stratum basale, the deepest layer of the epidermis, where stem cells and progenitor cells are constantly dividing through mitosis. Nutrients and oxygen are delivered to the newly formed cells by blood vessels in the dermis below.
Basal cells begin to divide and migrate upward, leaving behind a single sister cell to form new stem cells. The structure and function of the cells change and begin to differentiate as they move up through the epidermal layers.
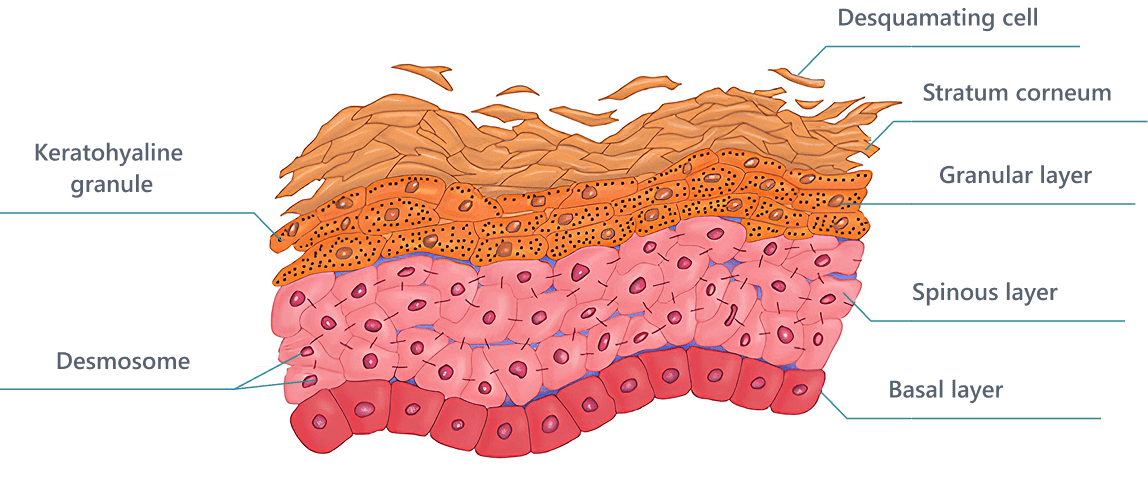
Layers of the epidermis include:
- The spinous layer, where cells begin producing the protein keratin.
- The granular layer, where cells flatten and form granules filled with keratin precursors and lipids. At this level, the cells lose their nuclei and organelles, and become more specialized as they begin to die.
- The lucidum layer, a thin, densely packed layer found in thicker skin like the soles of the feet.
- The stratum corneum – the outermost layer of fully keratinized dead cells that are flattened and overlap. The cells are packed with keratin and coated with lipids, forming a waterproof protective barrier.
The outermost layer of cells is continually sloughed off as new skin cells rise to the surface. In humans, the entire cycle, from cell formation to shedding, takes about a month, varying somewhat by age, health status, and location on the body.
Functions of the Human Skin
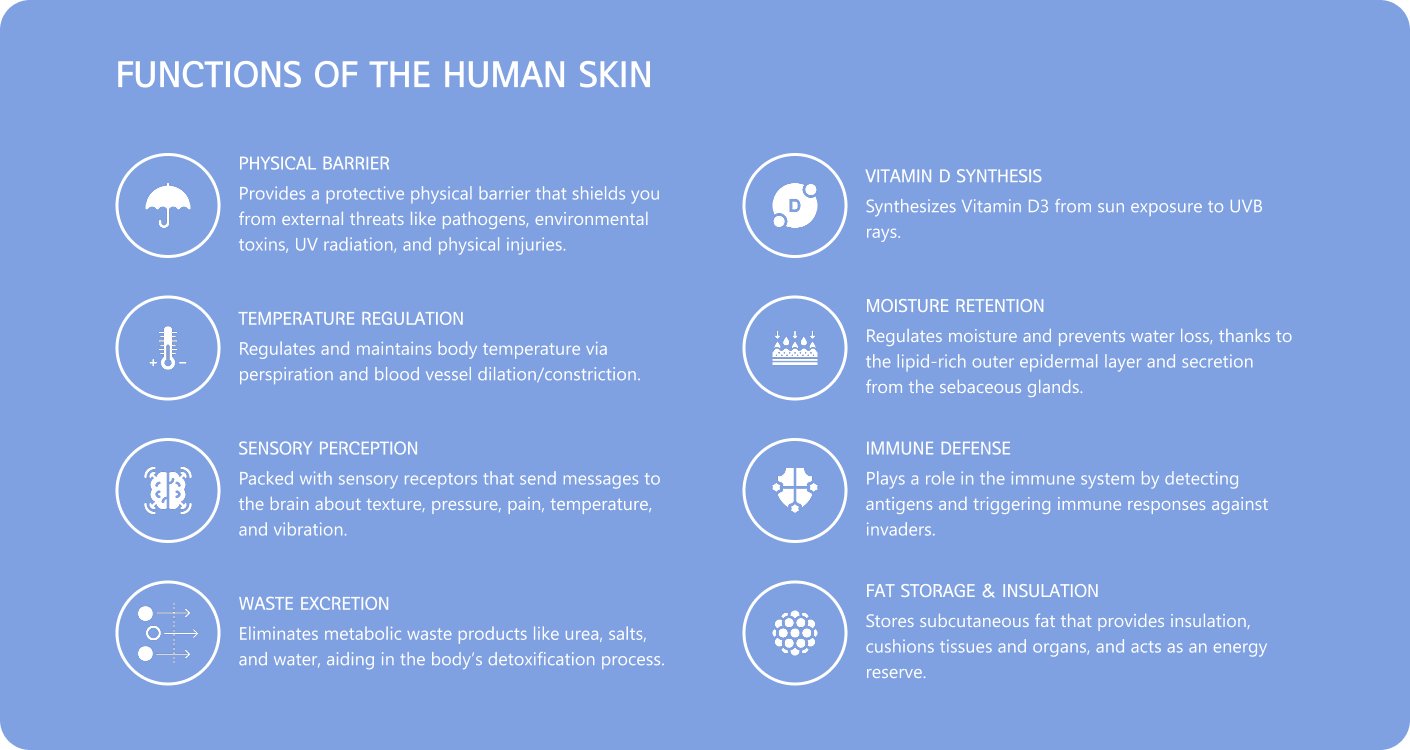
Your skin is more than just a pretty wrapping – it is one of your body’s most important vital organs, serving multiple critical functions:
- Provides a protective physical barrier that shields you from external threats like pathogens, environmental toxins, UV radiation, and physical injuries.
- Regulates and maintains body temperature via perspiration and blood vessel dilation/constriction.
- Packed with sensory receptors that send messages to the brain about texture, pressure, pain, temperature, and vibration.
- Eliminates metabolic waste products like urea, salts, and water, aiding in the body’s detoxification process.
- Synthesizes Vitamin D3 from sun exposure to UVB rays.
- Regulates moisture and prevents water loss, thanks to the lipid-rich outer epidermal layer and secretion from the sebaceous glands.
- Plays a role in the immune system by detecting antigens and triggering immune responses against invaders.
- Stores subcutaneous fat that provides insulation, cushions tissues and organs, and acts as an energy reserve.
The quality and function of skin cells is affected by factors like:
- Nutrition
- Hydration
- UV exposure
- Injury
- Disease
Most over-the-counter skin care products applied topically only affect the keratinized outer layers of dead skin cells in the stratum corneum, serving to hydrate, protect, and repair the skin’s natural barrier. However, some smaller molecules like retinoids and Vitamin C can penetrate deep into the live cells of the spinous layer, helping to stimulate cell turnover and providing antioxidant support. But topical skin care only makes a tiny dent compared to a nutrient-dense diet and optimal hydration.
How Glutathione Affects Skin Tone and Pigmentation
Glutathione is a super antioxidant that is essential to bright, healthy skin. Your body makes its own glutathione from the foods you eat, but modern diets and lifestyles often fall short of providing all the nutrients you need for optimal health. Supplementing with glutathione can help make up for dietary deficiencies.
Glutathione promotes bright and healthy skin in multiple ways:
- As an antioxidant, glutathione neutralizes free radicals – unstable molecules that can damage skin cells. By reducing oxidative stress, glutathione slows skin aging, marked by wrinkles, fine lines, and loss of elasticity. It also supports collagen and elastin proteins that give skin its firmness and elasticity.
- Glutathione helps to detoxify the body of harmful substances like heavy metals, chemicals, and pollutants. It binds to toxins to help eliminate them, preventing dull skin and acne caused by toxin buildup.
- Glutathione’s anti-inflammatory properties help to reduce skin puffiness and improve skin conditions like acne, eczema, and psoriasis, where inflammation plays a role.
- As an antioxidant, glutathione helps to repair damaged DNA and skin cell proteins, to support cellular turnover and regeneration.
- Glutathione regulates skin brightness and pigmentation by inhibiting production of melanin – a complex polymer molecule responsible for skin color. Melanin provides photoprotection by absorbing UV radiation, shielding cells from sun damage. It also promotes sun tanning, forms freckles and age spots, and causes uneven pigment in some people. Glutathione suppresses melanin production, causing dark spots and discoloration to fade over time.
Advantages of Glutathione IV Therapy
Glutathione is a tripeptide present in almost all living cells, made by the body from dietary nutrients like leafy vegetables, fruits, and nuts. Glutathione is also available as an oral supplement, and used to treat a wide range of skin and health conditions. But according to new research, a major drawback of oral glutathione is its low bioavailability in humans. However, when delivered by IV infusion, glutathione is broken down into its component amino acids and resynthesized in the cells.
Advantages of glutathione IV infusion therapy include:
- Quickly oxidized in the bloodstream
- Direct delivery to the cells
- Enhanced bioavailability
- Convenient alternative to oral supplements
Get Glutathione IV Therapy for Skin Lightening in NYC
Skin discoloration affects people of all ages, from all walks of life. Because your skin is part of what defines you, it plays a key role in how you see yourself, and how others perceive you. For that reason, skin care is a multi-billion dollar industry that continues to grow year-by-year. Yet skin care products are minimally effective compared to nutrition and hydration.
Glutathione IV therapy is an evidence-based solution for regulating skin pigmentation and promoting glowing, healthy skin. At Invita Wellness, glutathione is a popular choice for skin lightening and brightening. Glutathione’s anti-aging properties make it a perfect match for NAD+, Cryofascial, and other therapies known to promote youthful healthy skin.
Contact Invita Wellness today, and get ready to transform your skin from the inside-out with Glutathione IV therapy.
transform your skin from the inside-out
contact InVita Wellness today
Book Now
456 Broadway 2 Floor, New York, NY 10013, USA
Resources
Gandhi, Guneet, et al. “Glutathione: The master antioxidant–Beyond skin lightening agent.” Pigment International 8.3 (2021): 144-152.
https://journals.lww.com/pigi/fulltext/2021/08030/glutathione__the_master_antioxidant
Park, Kyungho. “Role of micronutrients in skin health and function.” Biomolecules & therapeutics 23.3 (2015): 207.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4428712/