Getting older is no picnic, no matter how hard you fight to ward off aging’s negative health effects. Cognitive decline in particular is a frightening prospect that most of us hope to avoid. But poor mental health is not an inevitable consequence of old age.
In recent decades, scientists have been striving to uncover the mysteries of aging, and they have identified multiple factors that accelerate the aging process. One key factor is glutathione, an anti-aging antioxidant that safeguards your physical and mental health.
Glutathione and Human Health
Glutathione is an antioxidant tripeptide made up of three amino acids, glycine, cysteine, and glutamic acid. It is the most abundant antioxidant in your body, produced within your cells from dietary amino acids. A person’s cellular glutathione levels are thought to be reliable indicators of longevity.
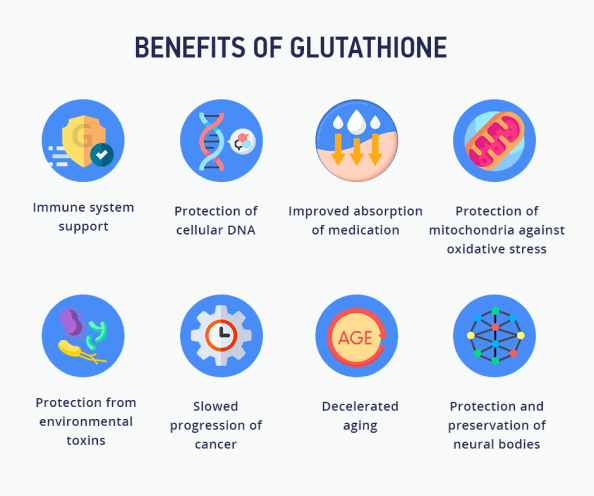
Some of the key benefits of glutathione include
- Immune system support
- Protection of cellular DNA
- Improved absorption of medications
- Protection of mitochondria against oxidative stress
- Protection from environmental toxins
- Slowed progression of cancer
- Decelerated aging
- Protection and preservation of neural bodies
Glutathione’s Anti-Aging Properties
Glutathione works to fight aging by reducing oxidative stress and preventing damage to cellular DNA. Chronic high levels of oxidative stress can lead to chronic inflammation, brain damage, cancer and other serious health issues. Glutathione also boosts the regeneration of antioxidant vitamins C and E.
Low glutathione levels allow free radicals to increase their activity throughout the body, accelerating the aging process and paving the way for cognitive decline. Low glutathione also weakens the immune system and has been linked to hospitalization and death from COVID-19.
Glutathione plays a major role in protecting cellular mitochondria, tiny organelles found in every cell that produce energy. Damaged mitochondria cause the body to slow down, reducing the efficiency and function of the body’s systems. In addition, damaged mitochondria emit free radicals, increasing overall oxidative stress and creating a downward spiral of declining health.
Because glutathione is produced within the cells, it is always at the ready to fight oxidative stress at the cellular level. When combined with vitamin C, vitamin E and selenium, glutathione teams up to destroy free radicals and combat aging.
Benefits of Glutathione for Alzheimer’s and Dementia
Multiple studies on aging recognize the relationship between antioxidant levels and age-related changes in the central nervous system. Free radicals and oxidative stress are thought to be responsible for neural changes that lead to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and dementia.
Supplementing your diet with glutathione and its precursors, NAC and L-cysteine, can help protect your brain and central nervous system from free radicals and oxidative damage. High-dose Vitamin C can help to support glutathione’s antioxidant properties.
How to Boost Glutathione at Any Age
Your body makes glutathione from amino acids found in the foods you eat. Eating a diverse and nutrient-dense diet can provide the amino acids and precursors you need to optimize your cellular glutathione production.
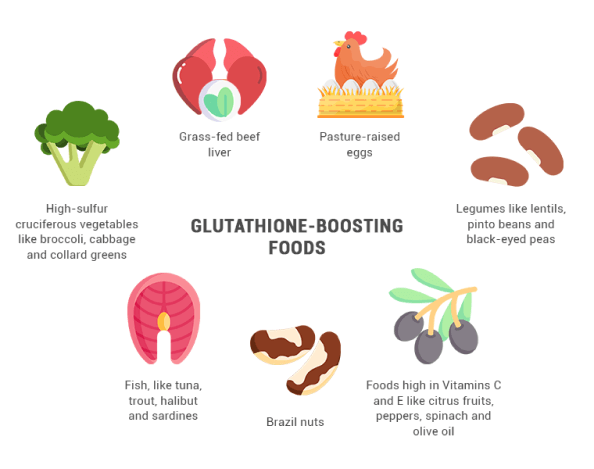
Top glutathione-boosting foods include:
- High-sulfur cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cabbage and collard greens
- Grass-fed beef liver
- Pasture-raised eggs
- Legumes like lentils, pinto beans and black-eyed peas
- Brazil nuts
- Fish, like tuna, trout, halibut and sardines
- Foods high in Vitamins C and E like citrus fruits, peppers, spinach and olive oil
Supplementing with N-acetylcysteine (NAC) is another way to boost glutathione production. NAC is a precursor to glutathione that also has protective properties for your respiratory health, helping you to clear mucus from your system. NAC is also effective for treating neurocognitive issues like substance addiction, behavioral disorders and bipolar syndrome.
Amino Acid and Glutathione IV Therapy in NYC
The fastest and most efficient way to boost your glutathione levels is to deliver glutathione and its precursors directly to your bloodstream via IV infusion. Oral supplements often lose their potency during the digestive process, and they sometimes pass right through your system without ever being absorbed. Intravenous supplementation ensures that the full potency of nutrients is preserved and delivered directly to your cells.
Since glutathione, NAC and amino acids are nutrients and not drugs, they are safe and effective, and you don’t need a medical prescription. In New York City, you can get amino acid IV therapy and glutathione IV therapy at InVita Wellness on Broadway. Contact InVita Wellness today and schedule your IV therapy session to combat aging and protect your cognitive health.
Resources
Chen, Jinghan Jenny, et al. “Altered central and peripheral glutathione in Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment: A meta‐analysis.” Alzheimer’s & Dementia 17 (2021): e054228.
Iskusnykh, Igor Y., Anastasia A. Zakharova, and Dhruba Pathak. “Glutathione in Brain Disorders and Aging.” Molecules 27.1 (2022): 324.