
Geopolitical factors aside, sovereign nations are defined by the populations that inhabit them, and by the social and cultural traditions handed down from one generation to the next. But in the 21st Century, multiple factors are blurring sociocultural lines, and native populations in developed countries are shrinking due to reduced fertility and low birth rates. In the United States, birth rates in 2025 are at an all-time low, according to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC).
One major factor affecting birth rates is an alarming drop in male testosterone levels. Impacting sperm count and quality, and interfering with the ability to sexually perform. Learn about factors affecting male testosterone and fertility, and evidence-based actions men can take now to reverse the trend.
What Defines Fertility and Birth Rate?
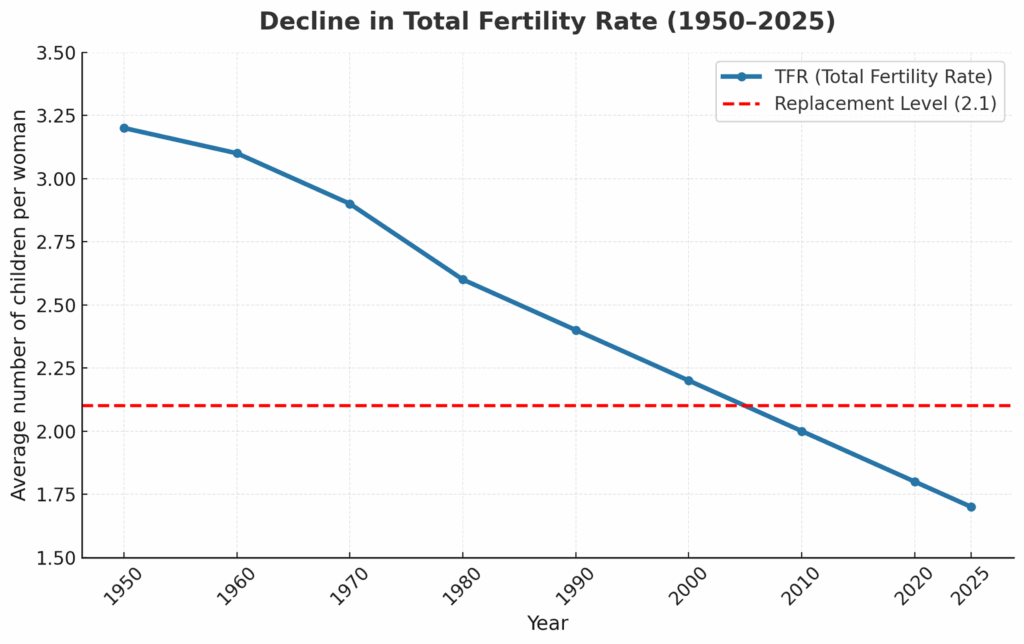
Fertility refers to the ability of humans and animals to conceive and produce offspring. Total fertility rate (TFR) is a metric that focuses on reproductive capacity and outcomes, expressed as the estimated average number of children a woman will have over her lifetime. To maintain a stable population in the 21st Century, TFR needs to be an average of 2.1 children per birth mother.
Birth rate is the actual number of live births per 1000 people in a population, over a given time span – typically calculated as births per year. It includes all people in a given population, not just women. In the United States and other developed nations, both fertility rates and birth rates have been declining steadily throughout the 21st Century, with TFR in the USA projected to be 1.7 children per birth mother in 2025 – a deficit of about half a child per couple, and a dramatic drop from 3+ children in the 1950s.
Many factors influence TFR and birth rate:
- Biological factors like age, health status and genetics.
- Sociocultural factors like marriage, birth control and abortion.
- Economic factors such as Income, education, and healthcare access.
- Public policy factors like maternity leave, childcare support, and incentives to have children.
At the current rate of population decline, scientists are sounding the alarm, warning that a collapsing population can have a far-reaching impact on everything from economic stagnation to erosion of social cohesion and loss of cultural heritage. While many young people in their reproductive prime are choosing to have fewer children or none at all, countless others are having difficulty conceiving and carrying a pregnancy to full term.
How Testosterone Influences Fertility Rates
Optimal total testosterone levels for healthy males aged 20-44 range from 600–900 ng/dL, with the cutoff for testosterone deficiency being 409-558 ng/dL, according to research published in the Journal of Urology. After peaking during the late teens and early 20s, male testosterone levels naturally decline with age. Levels below 500 ng/dL are associated with greater risk of type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and all-cause mortality.
Testosterone affects male fertility in multiple ways:
- Determines sperm count, quality, and motility – the ability of sperm cells to “swim” to reach a fertilized egg
- Drives libido and supports erectile function
- Regulates the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis, responsible for ongoing sperm production

The current averages for testosterone in the USA have declined to 450–600 ng/dL for young men, and even lower for older men. In addition to low sperm count and reduced fertility, symptoms of low testosterone include depression, hair loss and decreased libido. Scientists blame both environmental and lifestyle factors for the alarming drop.
Environmental Factors Affecting Male Fertility
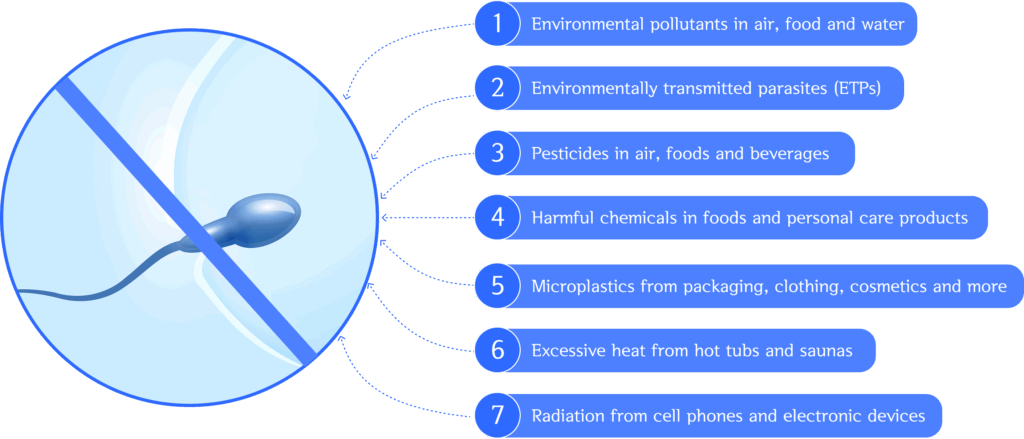
Scientists have identified a broad range of environmental factors that undermine sperm concentration, reduce total sperm count, and affect motility, and viability, while increasing abnormal sperm morphology and DNA fragmentation.
Environmental toxicity arises from exposure to:
- Environmental pollutants in air, food and water
- Environmentally transmitted parasites (ETPs)
- Pesticides in air, foods and beverages
- Harmful chemicals in foods and personal care products
- Microplastics from packaging, clothing, cosmetics and more
- Excessive heat from hot tubs and saunas
- Radiation from cell phones and electronic devices
Evidence from human and animal studies indicates a strong link between microplastic exposure and reduced male testosterone levels, and microplastics have been shown to accumulate in male reproductive organs. Yet it is almost impossible to avoid microplastics, as they are widely used in consumer and industrial products, and have infiltrated our food and water supplies. Even your underwear and workout clothes may be full of microplastics that affect your reproductive health.
Lifestyle Factors that Impact Testosterone Levels
In addition to exposure to environmental toxins, testosterone production and sperm quality is substantially influenced by lifestyle behaviors.
Lifestyle factors linked to low testosterone levels include:
- Excessive alcohol and tobacco use
- Prescription and recreational drugs and steroids
- Sedentary lifestyle and low muscle mass
- Prolonged sitting
- Wearing too-tight pants or underwear
- Obesity
- Chronic stress and anxiety
- Metabolic disorders like type 2 diabetes and chronic inflammation
- Nutrient-poor diet of ultra-processed foods
- Chronic sleep deprivation
- Online pornography consumption
- Lack of in-person social interactions with the opposite sex
In recent decades, the drop in testosterone levels correlates inversely with the rise in obesity. Excess body fat increases aromatase – an enzyme that converts androgens (male hormones) into estrogens (female hormones). In the United States, obesity rates have tripled since the 1950s while testosterone levels have progressively dropped.
Strategies for Boosting Male Testosterone
Despite its widespread prevalence, men who suffer from low testosterone and its unpleasant symptoms can take action to reverse the trend and restore healthy levels. Even implementing a few of the suggested strategies can make a difference.
Actions that can raise male testosterone:
- Avoid processed and refined foods, and opt for a whole foods, protein-based diet with plenty of animal protein from beef, lamb, fish and poultry.
- Avoid tap water and opt for natural spring water for drinking and cooking.
- Look for products with natural ingredients and fibers for personal care and clothing.
- Avoid excessive heat exposure in hot tubs and saunas.
- Protect your genitals from radiation from cell phones and laptops.
- Do 2-3 weekly sessions of heavy resistance training to naturally boost muscle mass and testosterone.
- Wear loose-fitting pants and underwear.
- Attain and maintain a healthy body weight.
- Get 7-9 hours nightly of high-quality sleep.
- Substitute online porn and social media for real-life interactions with the opposite sex.
Benefits of Testosterone Injection Therapy
In addition to taking precautions against toxins and making better lifestyle choices, testosterone injection therapy can help you raise and normalize your total testosterone levels.
Benefits of testosterone therapy include:
- Improved energy levels, reduced fatigue, and elevated mood.
- Increased lean muscle mass and improved strength.
- Enhanced libido and sexual function.
- Improved bone mineral density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
- Better cognitive function and memory.
- Improved cardiovascular health due to reduced fat mass and greater insulin sensitivity.
- Reduction in visceral and total body fat.

Before beginning testosterone therapy, have your levels checked and monitored by a healthcare provider. Avoid testosterone therapy if you have prostate issues or heart disease.
Boost Testosterone and Optimize Your Health with Invita Wellness NYC
Male testosterone levels are declining world-wide, but you don’t have to be a statistic – there are plenty of actions you can take to boost testosterone and improve fertility. In the process, you may enjoy the bonuses of robust health, improved appearance, and better self-esteem.
At Invita Wellness, we offer testosterone injection therapy, along with a wide array of other natural remedies and solutions for optimizing your health and quality of life. Contact Invita Wellness today, and take charge of your reproductive health and fertility with testosterone injection therapy in NYC.
Boost Testosterone in Soho NYC
contact InVita Wellness today
Book Now
456 Broadway 2 Floor, New York, NY 10013, USA
Resources
Hu, Chelin Jamie, et al. “Microplastic presence in dog and human testis and its potential association with sperm count and weights of testis and epididymis.” Toxicological Sciences 200.2 (2024): 235-240.
https://academic.oup.com/toxsci/article/200/2/235/7673133
Jacobs, Tim, et al. “Associations between online pornography consumption and sexual dysfunction in young men: multivariate analysis based on an international web-based survey.” JMIR public health and surveillance 7.10 (2021): e32542.
https://publichealth.jmir.org/2021/10/e32542/
Kumar, Naina, and Amit Kant Singh. “Impact of environmental factors on human semen quality and male fertility: a narrative review.” Environmental Sciences Europe 34.1 (2022): 6.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12302-021-00585
Leisegang, Kristian, and Sulagna Dutta. “Do lifestyle practices impede male fertility?.” Andrologia 53.1 (2021): e13595.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/and.13595
Mansour, Hend Abd El-Halim, and Al-Shaimaa Mohsen Sadek. “Impacts of environmental pollutants and environmentally transmitted parasites on male fertility and sperm quality.” Discover Applied Sciences 7.9 (2025): 1-24.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12302-021-00585-w
Skakkebæk, Niels E., et al. “Environmental factors in declining human fertility.” Nature Reviews Endocrinology 18.3 (2022): 139-157.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41574-021-00598-8
Zhao, Jing, et al. “Offline social capital, online social capital, and fertility intentions: evidence from China.” Humanities and Social Sciences Communications 11.1 (2024): 1-13.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41599-024-03643-9