
Technology has improved our lives in so many ways, opening new avenues for communication, education and entertainment, and connecting people across the globe in unprecedented numbers. But the downside of technological innovations is a world that runs at full speed, 24/7, making it hard for many of us to turn off our devices and get some sleep.
Ironically, round the clock access to every corner of the world has not made us more productive or prosperous. In fact, for many people, a constant influx of information has increased daily stress while depriving us of healthy sleep habits. To turn off the noise and normalize circadian sleep patterns, some people are turning to cryotherapy as a panacea for sleep disorders of every kind.
Sleep Deprivation is a Global Epidemic
Americans are known for our strong work ethic and dedication to high job performance, which in part explains our high levels of stress and poor sleep patterns. But new research shows that sleep deprivation has become a global epidemic, affecting millions. According to one source, total daily sleep has been reduced by up to two hours, world-wide.
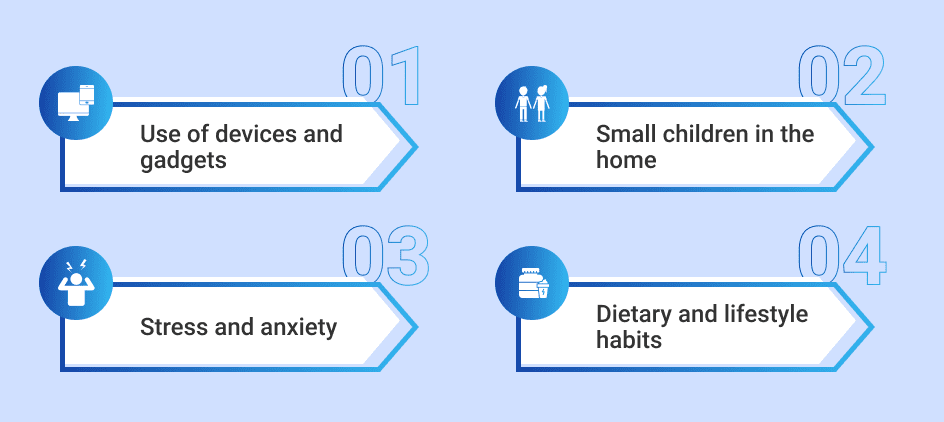
Factors driving the trend toward insufficient sleep include:
- Use of devices and gadgets: Technology is blamed for one in four cases of sleep deprivation in people aged 18-24. Our devices have also made us accessible to everyone, at any time, increasing stress and disrupting sleep.
- Small children in the home: Parenting small children often means disrupted and erratic sleep patterns.
- Stress and anxiety: For many, the stressors of work, family and daily living prevent a deep and restful night’s sleep. This is made worse by round-the-clock access by employers and co-workers.
- Dietary and lifestyle habits: Excess consumption of sugar, caffeine, alcohol, tobacco and other substances, along with lack of physical activity, can interfere with sleep.
Light pollution, exposure to environmental toxins, chemicals found in food, air and water and other man-made factors may also contribute to global changes in sleep patterns. Falling asleep with a television on can result in poor sleep quality. Staring at a computer screen right before bed can interfere with natural circadian rhythms that induce sleep. Shift workers who sleep during the day are highly subject to sleep deprivation.
Negative Effects of Sleep Deprivation
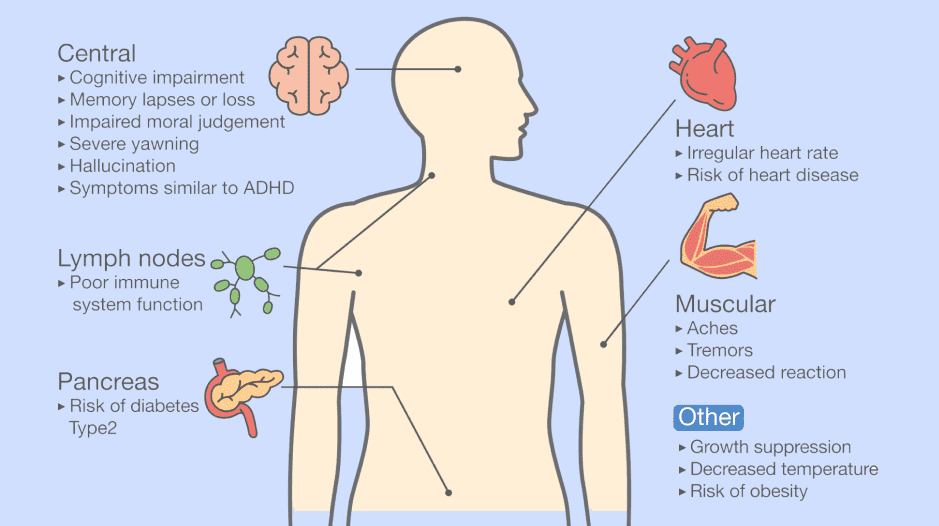
The negative health and social impacts of sleep deprivation are often understated. In fact, many metabolic health disorders have their roots in sleep deprivation. In most cases, we are treating the symptoms without getting at the source. Of the 15 leading causes of death in the US, sleep deprivation is linked to 7, including heart disease, blood clots, neurological disorders, diabetes, high blood pressure, septicemia and fatal accidents.
Other negative effects of sleep deprivation include:
- Obesity
- Cancer
- Reduced cognitive function
- Impaired memory
- Negative mood
- Poor job performance
- Poor academic performance
- Reduced reaction time
- Increased risk of industrial and traffic accidents
- Medical errors
- Lapses in judgement
Sleep Quality vs Quantity
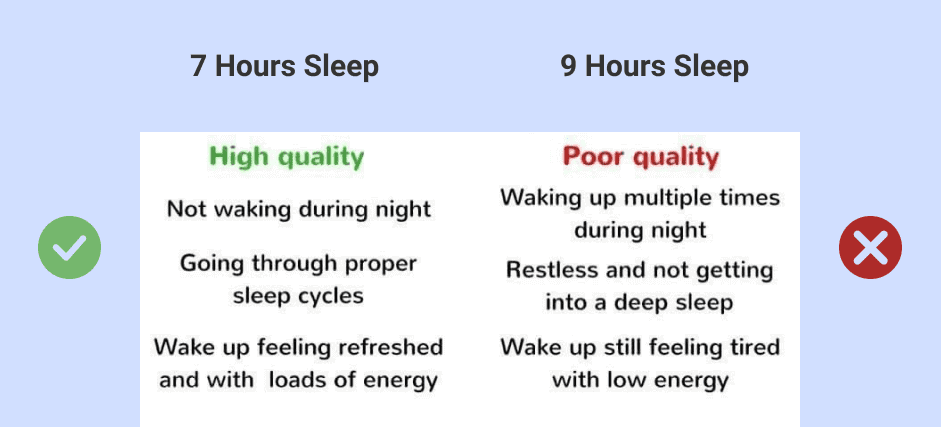
While sleep requirements vary from one person to another, it is largely agreed that adults need at least 7 to 8 hours of restorative sleep per night. However, sleep quality is even more important than quantity. Two separate studies of the sleep habits of college students both concluded that sleep quality surpasses quantity in terms of health, satisfaction with life and overall mood and wellbeing.
Sleep quality can be measured in terms of how quickly you fall asleep, how long you stay asleep, how often you wake up at night, and how quickly you get back to sleep after waking up.
In addition, quality sleep repeats a cycle of stages about every 90 minutes, progressing through three stages of non-REM sleep to a final stage of REM (rapid eye movement) sleep.
Stages in the sleep cycle are:
- N1: During the N1 transition phase from wakefulness to sleep, you may have lucid dreams and remain semi-aware of your surroundings.
- N2: As you move from N1 to N2, your breathing and heart rate slow. About half of your total sleep time is spent in the N2 stage.
- N3: The N3 stage is critical for the healing and repair of tissues throughout your body.
- REM: The REM stage is the dream stage of sleep, occurring about every 90 minutes throughout the night. Your brain is highly active during REM sleep, and your eyes move about rapidly. Paralytic chemicals are secreted during REM sleep to prevent you from acting out your dreams.
The duration of each stage varies from one cycle to the next throughout the course of the night. However, many people with sleep disorders cycle between stages N1 and N2, without achieving adequate amounts of deep N3 and REM sleep.
Whole Body Cryotherapy Promotes Better Sleep

During a whole body cryotherapy session, your entire body is encased in a cryochamber and exposed to an icy stream of nitrogen gas, cooling the chamber to sub-freezing temperatures as low as -166º Fahrenheit.
Abrupt exposure to extreme cold triggers a series of physical reactions:
- Blood vessels at the body’s surface constrict, shunting blood to the internal organs and elevating core temperature.
- Your brain signals the release of endorphins, feel-good hormones that boost mood and reduce anxiety.
- The immune system is stimulated and strengthened.
- The body feels refreshed and rejuvenated.
Regular cryotherapy sessions have proven effective for treating and curing primary and secondary insomnia. In addition to other health benefits of cryotherapy, you will reap the many benefits of deep restorative sleep.
Chill Out for Better Health in NYC
If you have trouble sleeping in NYC, cryotherapy is just around the corner. A 3-minute whole body cryotherapy session has multiple health benefits, including reduced fatigue, more energy, improved circulation and better immune function. Most importantly, just 3 minutes of whole body exposure to an icy-cold environment promotes deep restful sleep.