
Inflammation is a natural response by your immune system to injuries, pathogens or disruptions that upend your body’s homeostasis — the resting state of balance where everything functions as it should, and hormones and chemicals are at optimal levels. Inflammation can be an acute response to a temporary disruption, or it can become chronic, remaining elevated when a perceived threat does not subside over an extended period of time.
Learn how cryotherapy for chronic inflammation can help calm your immune response and promote optimal metabolic health, and how local cryotherapy can help promote healing in cases of acute inflammation.
Symptoms of Acute and Chronic Inflammation
Inflammation is your body’s natural response to any perceived threat. During an inflammatory response, your blood vessels dilate to deliver white blood cells and fluids to the extracellular spaces surrounding the affected site.
Acute Inflammation
Acute inflammation occurs as a result of a single incident, such as an injury or superficial wound. Fluids, nutrients and white blood cells are rushed to the site of injury to ward off bacteria and stimulate the healing process. Acute inflammation typically abates in a matter of hours or days.
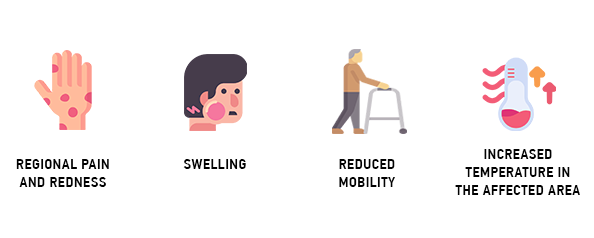
Symptoms of acute inflammation include:
- Regional pain and redness
- Swelling
- Reduced mobility
- Increased temperature in the affected area
Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is more insidious, hanging on for months or even years. With chronic inflammation, the body retains excess fluids in the interstitial spaces between cells and in the joints, making you feel puffy, achy and bloated.
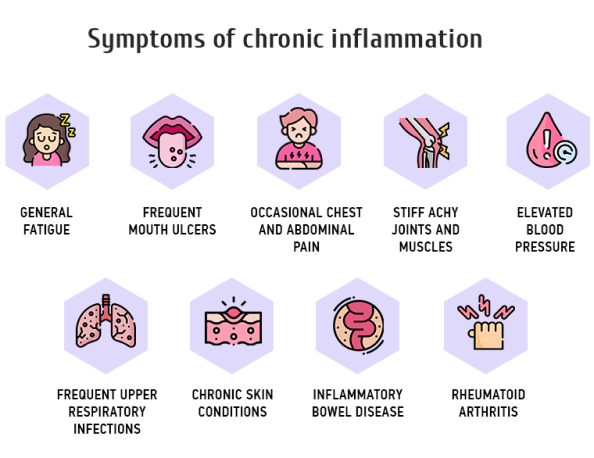
Symptoms of chronic inflammation include:
- General fatigue
- Frequent mouth ulcers
- Occasional chest and abdominal pain
- Stiff achy joints and muscles
- Elevated blood pressure
- Frequent upper respiratory infections
- Chronic skin conditions like acne or psoriasis
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Rheumatoid arthritis
Causes of Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is often a common denominator in metabolic, neurocognitive and neurodegenerative disorders, and is thought to be a key contributing factor to a broad spectrum of diseases. Acute inflammation can be brought on by a wound or injury, or as a result of a surgical procedure. In both cases, cryotherapy for inflammation can be a helpful option for easing symptoms, reducing pain and promoting better health.
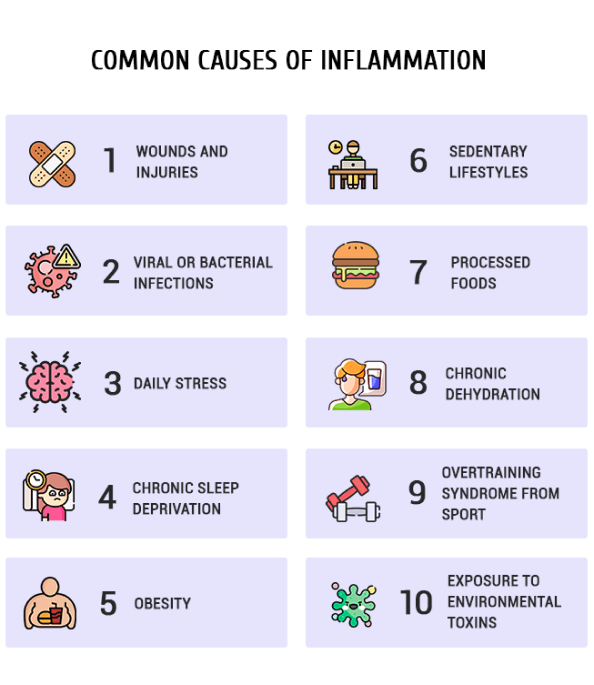
Common causes of inflammation include:
- Wounds and injuries, where soft tissues and bones are damaged from trauma or surgery
- Viral or bacterial infections
- Daily stress that evokes a fight-or-flight response
- Chronic sleep deprivation
- Obesity, where inflammatory cytokines are produced by excess body fat
- Sedentary lifestyles that slow down metabolic processes and cause systemic dysfunction
- Processed foods loaded with salt, sugar and chemicals
- Chronic dehydration that causes the body to hold onto fluids at all costs
- Overtraining syndrome from sports or exercise
- Exposure to environmental toxins in the air, water and food
For the most part, chronic inflammation is a lifestyle-related condition. Its progression can be halted and reversed by modifying your daily habits regarding stress, sleep, nutrition, exercise and exposure to environmental toxins.
Whole Body and Local Cryotherapy for Inflammation
Cryotherapy is an ages-old approach to treating inflammation. Early use involved cold water, snow and ice to bring about a therapeutic effect. After refrigeration became available, ice packs and ice baths were used. Today, modern technology has ushered in the use of liquid nitrogen to surround inflamed tissues with an icy blast of sub zero temperature gas.
During a cryotherapy session, exposure to extreme cold causes blood vessels to contract, shunting fluid away from superficial tissues and numbing nerve endings. The body’s response to cryotherapy is a protective mechanism that prioritizes blood flow to the vital organs, in the event that cold exposure poses a dire threat. As the body warms again, excess fluids are eliminated via the kidneys, while healthy blood flow is restored to the superficial cells.
Cryotherapy is a safe and effective treatment for both acute and chronic inflammation.
- Local cryotherapy is often used in conjunction with physical therapy to reduce inflammation and numb pain from acute injuries and surgical procedures. During a local cryotherapy session, nitrogen gas is streamed from a wand-like device to target the inflamed tissues. Local cryotherapy may also be effective for reducing inflammation from rheumatoid arthritis.
- Whole body cryotherapy is used to treat generalized systemic inflammation, and can be effective for promoting the removal of excess fluids. In addition, WBC evokes the release of endorphins, feel-good hormones that can help manage stress and improve sleep quality. Athletes and fitness enthusiasts often rely on WBC to promote recovery from intense training.
- Cryo Facial is a cosmetic treatment that uses cold therapy to eliminate facial puffiness and promote a more robust collagen matrix for improved skin elasticity.
Enjoy Whole Body and Local Cryotherapy in NYC
Whether you are injured, stressed out, or need a boost for better health, the therapeutic benefits of cryotherapy are nearby at InVita Wellness. Regular cryotherapy sessions can help you look younger, feel more energetic and improve your overall health. Contact InVita Wellness today, and take charge of your health for a better overall quality of life.
Resources:
Pahwa, Roma, Amandeep Goyal, and Ishwarlal Jialal. “Chronic inflammation.” StatPearls [Internet] (2021).