
Whether you’re an athlete, a runner or a dedicated gym rat, you know how hard it is to consistently maintain a high level of performance, day after day, especially as you get older. Recovery, sleep, nutrition and hydration all play a role, but when your performance nosedives into a downward spiral, you may benefit from NAD therapy.
A growing body of research points to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) as an essential cofactor in energy production, aging, and a broad range of metabolic processes that affect physical performance. Supplementing via NAD IV drip can help to restore peak performance and prevent age-related decline.
What Makes NAD so Important
NAD (and NAD+, its oxidized form) is a coenzyme found in every living cell. NAD plays a key role in a broad range of metabolic processes, and serves as a synergist for proteins that govern biological activity.
Some major benefits of NAD supplementation include:
- Enhances conversion of food to energy
- Supports mitochondrial production of ATP — the energy molecule
- Plays a key role in DNA repair
- Helps repair damaged blood vessels
- Improves muscle function
- Boosts metabolism and combats unwanted weight gain
- Slows and reverses the aging process
- Helps to regulate circadian rhythms, for better sleep
- Enhances mental clarity and cognitive function
- Boosts energy and combats fatigue
Despite its importance, your body makes less and less NAD as you begin to age beyond your reproductive prime. In fact, declining levels of NAD and concurrent deterioration of mitochondria are thought to be primary contributors to aging.
How NAD Impacts Exercise Performance
While the functions of NAD in the body are multifaceted, its role in the mitochondria may have the greatest impact on exercise performance.
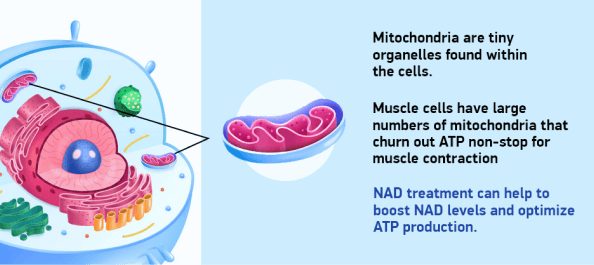
Mitochondria are tiny organelles found within the cells. You can think of them as little energy factories that use oxygen to convert fats and carbohydrates to fuel for cellular processes.
In physically active people, muscle cells have large numbers of mitochondria that churn out ATP non-stop for muscle contraction. In fact, regular exercise increases the size and number of mitochondria in muscle cells, enabling athletes to continually improve their performance.
But when NAD is depleted, the mitochondria are unable to function at their peak, because NAD is an essential molecule in the series of chemical reactions that break down glucose to generate ATP, an ongoing process called the Krebs cycle. NAD treatment can help to boost NAD levels and optimize ATP production.
A Study on NAD and Cardiovascular Fitness in Runners
To illustrate the importance of NAD in aerobic exercise performance, researchers studied the impact of daily NAD supplementation in four groups of young and middle-aged recreational runners.
Participants were given a daily oral supplement of nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), the immediate precursor to NAD+ that prompts the body to produce NAD.
- Group one, the control group, was given a placebo
- Group two was given a low dose of 300mg per day
- Group three got a moderate dose of 600mg per day
- Group four was the high-dose group, given 1200mg per day
Each group had 10 male and two female runners who trained daily for 40 to 60 minutes, five to six days per week. The study continued for six consecutive weeks.
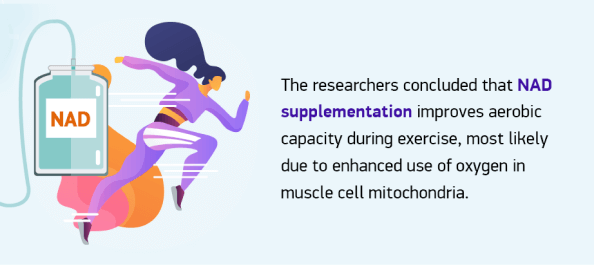
Cardiovascular fitness testing was performed before and after the intervention to measure total volume of oxygen uptake (VO2), percentage of maximum oxygen uptake (VO2max), and power at first and second ventilatory thresholds. After the intervention, all four markers increased in the moderate and high dosage groups compared to baseline.
The researchers concluded that NAD supplementation improves aerobic capacity during exercise, most likely due to enhanced use of oxygen in muscle cell mitochondria.
Another Study on NAD+ and Resistance Training in Middle-Aged Adults
In addition to declining levels of NAD as we age, humans begin to lose lean muscle mass, a condition called sarcopenia. In this study, researchers set out to see if resistance training had an effect on NAD+ levels in the muscle tissues of middle-aged adults.
The study participants were 16 untrained adults aged 55-63. At baseline, participant levels of skeletal muscle markers related to NAD+ were measured. Results were compared to the same markers in a cohort of 15 recreational-trained males aged 19 to 25.
The study group underwent 10 weeks of total-body resistance training, two days per week. At the end of the intervention, markers for NAD+ were compared to baseline markers, and to the same markers in the younger cohort.
Results of the study suggest that resistance training in middle-aged participants helps to restore muscle NAD+ to levels similar to those of younger fit individuals.

NAD Treatment for Improved Fitness and Exercise Performance
Regular aerobic exercise and resistance training are the most effective ways to safeguard your health and offset the negative effects of aging. Supplementing with NAD can help you get the most from your exercise program.
Intravenous infusion is the most effective way to optimize your NAD levels. Delivery via NAD IV drip ensures that NAD is transported directly to your muscle cells, bypassing the digestive tract where oral supplements often lose much of their potency. Regular NAD therapy sessions can help you maintain peak fitness while giving you an extra hedge against aging.
NAD Therapy in NYC
Staying active as you age is critical, and research suggests that declining performance is not inevitable. To ensure that you have the energy you need to maintain optimal fitness, you need to give your body the nutrients it needs to repair damaged DNA and build new healthy cells with functional mitochondria.
InVita Wellness is dedicated to helping you stay young, fit, healthy and beautiful at any age. Our menu of IV nutrient cocktails, local and whole body cryotherapy, and nutrient injection therapies is designed to meet your needs for health, exercise recovery and performance. Contact InVita Wellness today, and schedule your NAD IV drip session, to restore youthful vitality.
Resources
Lamb, Donald A., et al. “Resistance training increases muscle NAD+ and NADH concentrations as well as NAMPT protein levels and global sirtuin activity in middle-aged, overweight, untrained individuals.” Aging (Albany NY) 12.10 (2020): 9447.
Liao, Bagen, et al. “Nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation enhances aerobic capacity in amateur runners: a randomized, double-blind study.” Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition 18.1 (2021): 1-9.