In America, drinking alcohol serves as a rite of passage for young people as they explore the forbidden fruits of adulthood. Despite widespread abuse among teenagers and on college campuses, most people acknowledge this period as a temporary phase, and don’t expect to become addicted. But some people are more vulnerable to alcohol addiction than others, and before long they find it impossible to quit.
Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms
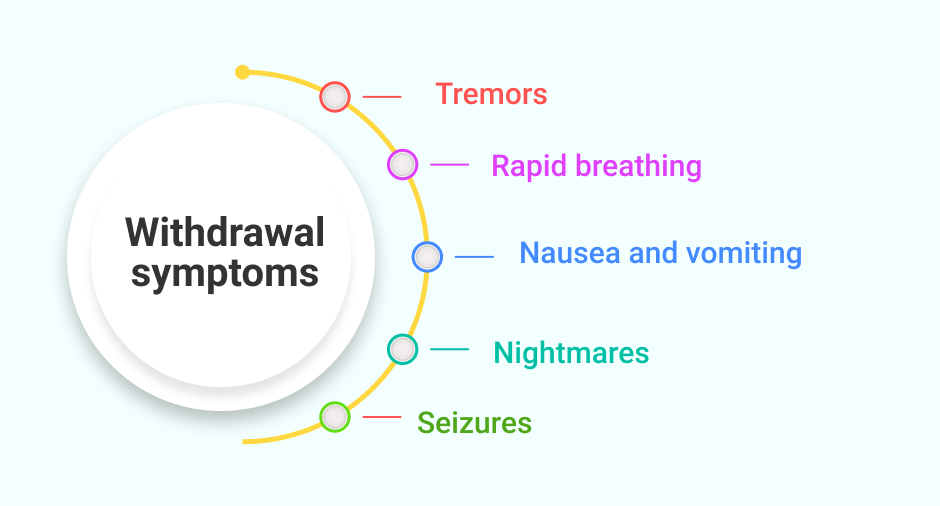
What begins as a seemingly harmless recreational activity in youth can become a serious physical addiction over time. Attempts to detox from alcohol can mean brutal days of nausea, sweating and even hallucinations. Recovery from a relapse can be even harder than the initial withdrawal, because the sufferer knows what symptoms are in store.
Withdrawal symptoms may include some or all of the following:
- Tremors
- Rapid pulse
- Increased blood pressure
- Rapid breathing
- Sweating
- Nausea and vomiting
- Anxiety
- Irritability
- Nightmares
- Insomnia
- Hallucinations
- Seizures
- Delirium tremens (sudden severe nervous system changes)
Alcohol withdrawal symptoms normally diminish within five days, although a small percentage of people may experience symptoms for weeks after quitting alcohol.
Understanding Alcohol Addiction

Alcohol consumption is common in most cultures around the world and has been for centuries. Yet not everyone who drinks becomes addicted. In fact, only 10 to 15 percent of people who consume alcohol develop problems with dependency. We do know that some people have a higher predisposition to become alcohol dependent.
Certain populations are at higher risk for alcohol dependency:
Men are much more likely to become alcohol dependent than women, with up to half of American men having some sort of alcohol-related problem.
College students often use alcohol as a social lubricant, for stress-management, or in response to peer pressure. Habits begun in college often carry over into adulthood.
Children with a history of physical or psychological abuse, and children of alcohol-dependent parents, are more likely to abuse drugs and alcohol and become alcohol dependent.
Mentally ill people with disorders like schizophrenia or bipolar disorder often have substance abuse problems as well.
Native Americans tend to have high rates of alcohol dependency. Genetics and poverty are often cited as underlying causes.
While the exact mechanisms of alcohol addiction are uncertain, researchers are getting closer to uncovering certain characteristics that may increase the risk of alcohol dependency.
A 2018 study used laboratory rats to try to isolate anomalies in those that became alcohol dependent. They found that alcohol addicted rats had an impaired brain mechanism that resembled that found in post-mortem brain tissue of alcohol dependent humans. The mechanism, gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA), affects brain cells in the amygdala, a region of the brain that regulates memory, learning, motivation and emotions. GABA inhibits brain cell signaling in the central amygdala.
Withdrawal from Alcohol Addiction
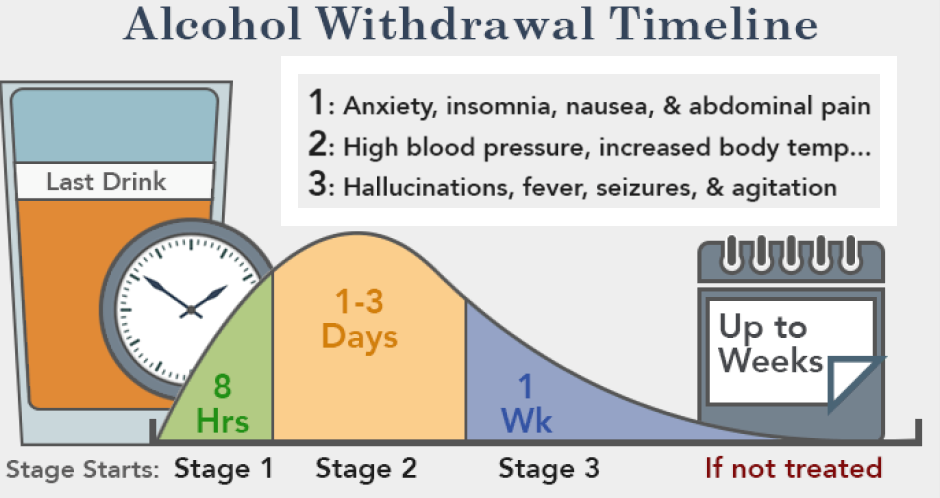
When you ingest alcohol, it immediately alters your metabolic chemistry, exciting neurotransmitters and hormones to respond and restore balance. It is your liver’s job to process and eliminate toxic substances like alcohol from your system. However, when you drink on a daily basis, you not only tax your liver, but your body chemistry begins to reconfigure, to accommodate the altered chemical state brought on by alcohol.
Alcohol is considered a depressant, meaning it slows down your brain. With regular alcohol exposure over time, your brain adapts to its altered chemical state by producing large amounts of stimulating chemicals like serotonin and norepinephrine. When you suddenly stop ingesting alcohol, elevated levels of stimulating hormones remain for some time in your circulatory system, leading to withdrawal symptoms.
In severe cases, withdrawal may bring on delirium tremens, a dangerous metabolic state where the brain does not adjust its chemistry smoothly once alcohol consumption is stops. A state of temporary confusion ensues, accompanied by life-threatening changes in circulation and breathing. Heart rate and blood pressure may become erratic, increasing the risk of stroke or heart attack.
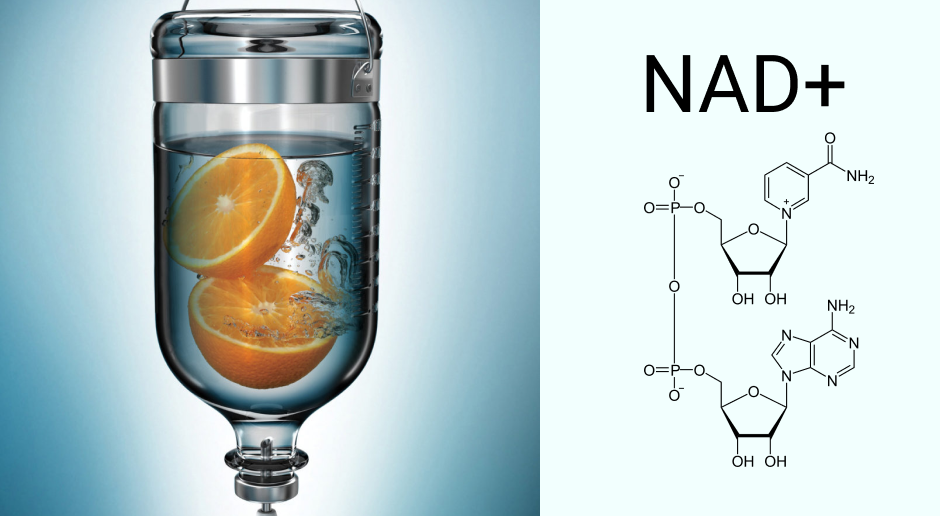
The Role of NAD+ in Restoring Metabolic Balance
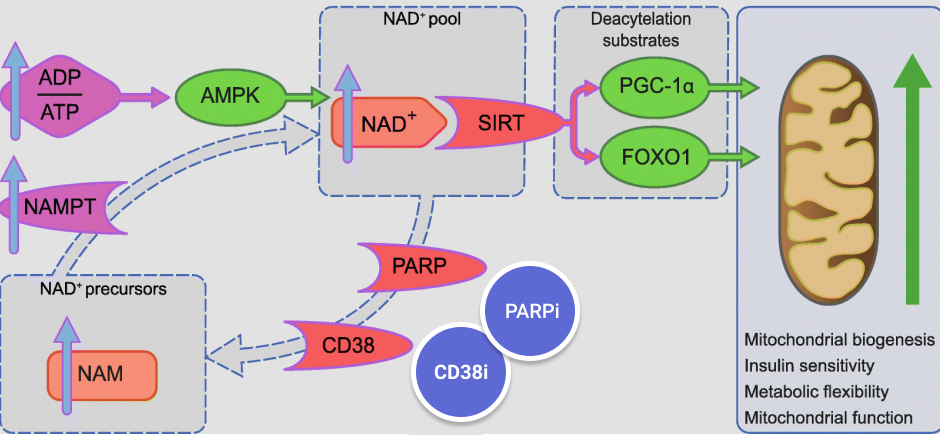
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) is a metabolic co-enzyme that plays a critical role in structuring, repairing and remodeling cells throughout your body. NAD+ is an all-natural enzyme that serves as a neurotransmitter, sending signals that stimulate energy production and other vital intracellular functions. NAD+ must be replenished on a daily basis from dietary sources. Specifically, NAD+ is a derivative of Vitamin B3, also known as niacin, found in many common foods.
Drug and alcohol abuse cause chemical changes in the brain that reorganize it on the cellular level. Neurotransmitters like NAD+ become depleted as the brain becomes damaged from substance abuse. NAD+ therapy replenishes the vital neurotransmitter and mitigates the severity of symptoms during the course of withdrawal.
NAD+ Alcohol Detox Treatment

If you suffer from alcohol addiction and have tried repeatedly to quit, the natural coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) may offer a way to withdraw with minimal discomfort. Patients undergoing alcohol detox treatment with NAD+ are able to quit using alcohol without enduring days of grueling symptoms. NAD+ alcohol detox treatment is safe, effective and FDA approved.
The most effective way to replenish NAD+ is via IV drip. When combined with a specific amino acid complex, NAD+ IV therapy can result in profound, complete and lasting recovery from alcohol dependency with minimal discomfort from withdrawal symptoms.
The IV therapy protocol usually entails one NAD+/amino acid complex infusion per day, for 10 consecutive days. Dosages are individualized to ensure you get the exact amount of nutrients you need for successful detox. In many instances, withdrawal symptoms begin to subside within minutes of the first infusion.
NAD+ IV Alcohol Detox in NYC
Making the decision to walk away from alcohol dependency is a bold and courageous move. NAD+ infusion therapy can make the alcohol detox process easier and less painful than trying to quit on your own. Compared to other detox methods, NAD works rapidly, reducing withdrawal symptoms and physical cravings within three to four days, and significantly reducing the discomfort of the withdrawal process.
If you are ready to change your life and detox your body from alcohol, contact Advanced Cryo NYC today. Our friendly staff of medical professionals will make the detox process as smooth and comfortable as possible. Get rid of alcohol addiction and get your life back on track with Advanced Cryo NYC.
Resources
Augier, Eric, et al. “A molecular mechanism for choosing alcohol over an alternative reward.” Science 360.6395 (2018): 1321-1326.