Good health relies on numerous biological processes that govern human metabolism. Most of us take our health for granted, as long as we feel good and have sufficient energy to perform everyday activities. But as we age, we often experience a decline in physical performance as our risk of metabolic disease goes up.
Scientific research on aging has uncovered the power of a tiny coenzyme called nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, or NAD+, found in every cell throughout the human body, and in the cells of all living things. NAD+ performs many functions that help maintain healthy cells, and it plays a key role in DNA repair. Without NAD+, life would not exist.
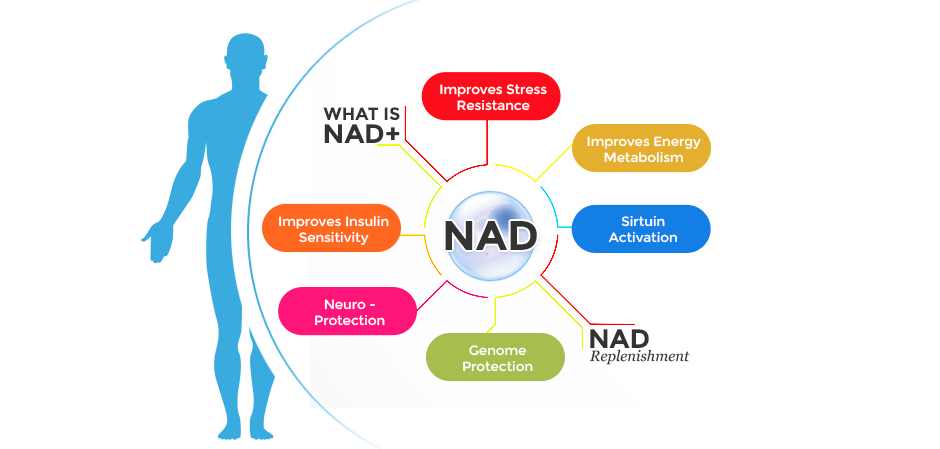
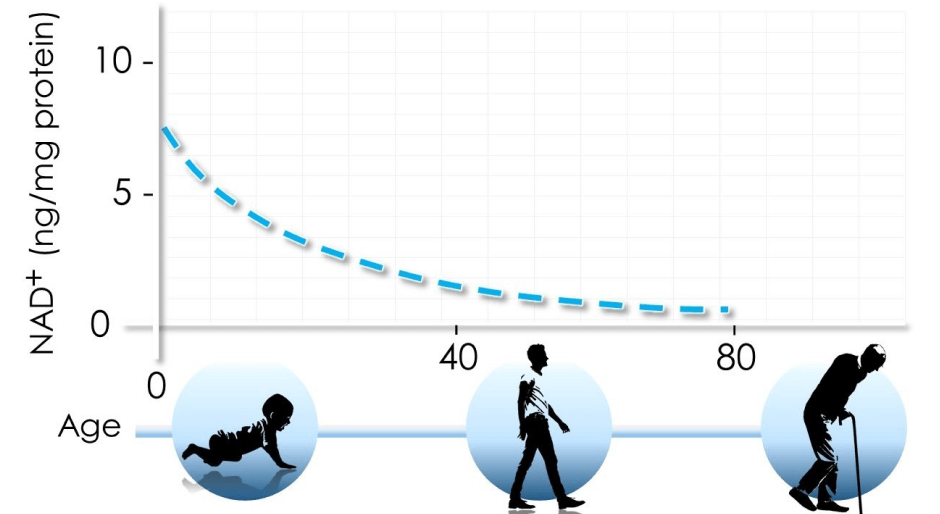
As you age beyond your reproductive prime, your NAD+ levels naturally decline. Paradoxically, you need more NAD+ as you get older to maintain good health and avoid degenerative diseases. Certain foods provide precursors to NAD+ that help your body manufacture it, but even the healthiest diet cannot provide enough of the necessary precursors to optimize NAD+ levels in middle aged and older adults.
NAD+ to Combat Muscular Sclerosis
NAD+ is essential for energy production in your body’s cells. It works within your mitochondria, tiny organelles located inside each cell that use oxygen and glucose to create ATP, the energy molecule. The NAD+ coenzyme also works as a helper molecule for certain proteins that regulate a broad range of biological processes. NAD+ plays an important role in cell signaling and in the repair of DNA damage caused by free radicals and various environmental factors.
Increased cellular levels of NAD+ have been shown to:
- Boost energy production and use.
- Speed up cellular repair.
- Coordinate circadian rhythms that regulate sleep.
- Improve mental clarity.
- Reduce chronic fatigue.
- Reduce symptoms and slow progression of neurological disorders like MS, Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease.
- Support and speed recovery from alcohol and drug addiction.
The metabolism-boosting effects of NAD+ may help you achieve and maintain a healthy weight, since a more active metabolism burns more calories.
NAD+ and Aging
Getting older is often characterized by metabolic dysfunction and frailty. Reduced levels of NAD+ have been shown to play a key role in the metabolic decline associated with aging.
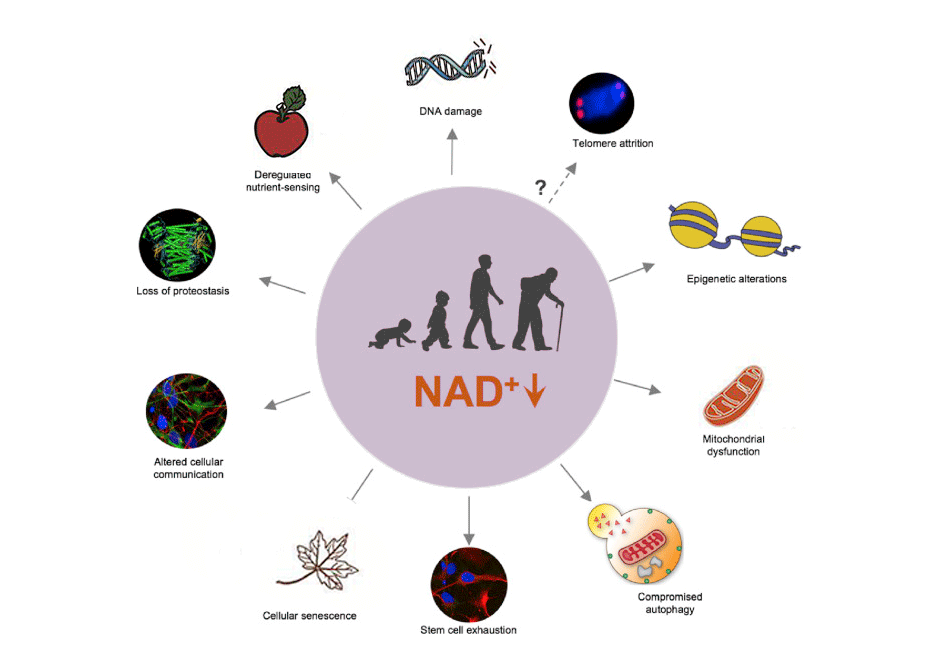
Common physical changes that come with aging include:
- Reduced elasticity and buildup of fatty deposits in blood vessels
- Reduced muscle mass (sarcopenia) and lower bone mineral density (osteoporosis)
- Stiffer joints with reduced range of motion
- Slower digestion
- Reduced vital organ function
- Impaired vision and hearing
- Changes to hair, skin and nails
- Increased body fat percentage
Scientists have isolated an element called NADase CD38 that appears to destroy NAD+ in aging bodies. In a recent study conducted on mice (Tarragó et al. 2018), researchers administered 78c, a potent CD38 inhibitor, which resulted in elevated levels of NAD+ in the study subjects.
After treatment, the research team observed an improvement in multiple metabolic aging parameters, including improved glucose tolerance, increased exercise capacity and better heart function. The treatment also inhibited several pathways that negatively affect health span, and reduced DNA damage associated with cellular aging.
NAD+ therapy has been shown to slow and even reverse some symptoms of aging through several mechanisms. In addition to reducing and inhibiting metabolic disorders, NAD+ helps reduce age-related inflammation responsible for cellular damage and a host of metabolic and neurological disorders. NAD+ also appears to inhibit age-related macular degeneration of the retina, responsible for impaired vision in the elderly.
NAD+ and Neurological Conditions
In the past, degenerative disorders of the central nervous system (CNS) have most often been associated with advanced old age. However, the incidence of neurodegenerative disorders is not only growing in number, but it is occurring in more people at a younger age. Depletion of NAD+ appears to be a major contributing factor to neurodegenerative diseases.
Alzheimer’s disease and NAD+
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a common form of dementia that affects tens of millions of people around the world. The incidence of AD is projected to double over the next 20 years. The disease is characterized by reduced cognitive function, loss of memory and reduced emotional control. Symptoms worsen over time, and gradually lead to death.
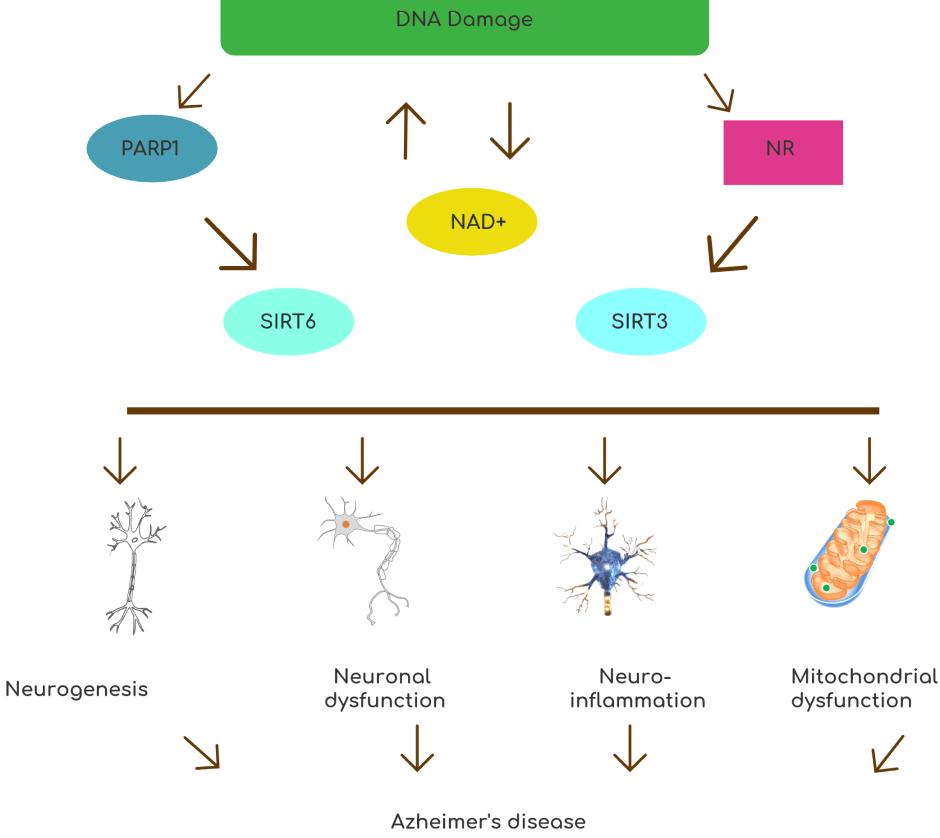
Like Parkinson’s and MS, AD is an autoimmune disorder marked by inflammation of key neurons and elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines. Cytokines are signaling molecules released by the immune system to fight invading pathogens. However, in the case of autoimmune disorders, cytokines attack the body’s own healthy cells.
In another mouse study (Hou et al. 2018), NAD+ supplementation with nicotinamide riboside (NR), a precursor to NAD+, significantly reduced inflammation of neurons while improving motor function, memory and learning in mice with AD-like symptoms.
Parkinson’s disease and NAD+
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is another neurodegenerative disorder that was once associated with advanced old age. Today, the condition is appearing in a much younger populations, often affecting people in their 50s and 60s. Parkinson’s disease is caused by the destruction of dopamine-producing neurons.
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter, a chemical released by nerve cells to signal other nerve cells. Dopamine is essential for CNS functions like motor control, mood, attention, motivation and pleasure. Low levels of dopamine are responsible for the loss of motor control and other symptoms seen in Parkinson’s patients. In addition to PD, dopamine plays a role in a number of other physical and psychological disorders.
Recent research reveals that dysfunction in the mitochondria (the organelles where the cells produce energy) may be a contributing factor to the cascade of events that leads to the destruction of dopamine-producing neurons, and ultimately to symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. There is no known cure for Parkinson’s disease, and to date, pharmaceutical solutions are limited and their effects are short-lived.

The effect of NAD+ in supporting and repairing mitochondrial DNA holds promise for treatment of Parkinson’s symptoms and for slowing the progression of PD.
For more information about NAD+ treatment for Parkinson’s disease, follow this link
NAD+ Combats Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is also a neurodegenerative autoimmune disorder that affects the central nervous system (CNS), causing physical and psychological symptoms for MS patients. MS affects about 2.5 million people worldwide. Like Parkinson’s and Alzheimers, there is no known cure for MS, but recent research suggests that NAD+ therapy can reduce symptoms and slow the disease’s progression.
In MS patients, autoantibodies attack and destroy protective myelin-producing cells that surround neurons. Since neurons govern motor control and send information via the CNS, damaged neurons have a profound effect on both mobility and cognitive function.
In yet another mouse study (Tullius et al. 2014) NAD+ was found to block a condition in mice called autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), a mouse model of MS. In the experiment, NAD+ reversed progression of the disease by restoring myelin cells and regenerating nerve cells.
There is no cure for MS, but treatments like NAD+ therapy appear to reduce the intensity of symptoms and slow the rate of progression.
NAD+ therapy holds enormous promise for the treatment of many diseases and disorders, and it is no wonder, since NAD+ plays such a vital role in healthy cell function.
For more details on how NAD+ IV therapy can help with the symptoms of MS, follow this link: New Therapies for Multiple Sclerosis Treatment with NAD+
NAD+ and Substance Addiction
People suffering from alcoholism and addiction to opioid drugs have long been stigmatized by society, and addiction has often been viewed as a moral issue. However, with a growing crisis of substance abuse among people from all walks of life, addiction is finally being recognized and treated as an important health issue that impacts us all.
Chronic use of drugs and alcohol depletes NAD+ levels in your cells, inhibiting energy production and slowing your metabolism. On the flip side, there is evidence to suggest that people with naturally low levels of NAD+ may be more susceptible to addiction.
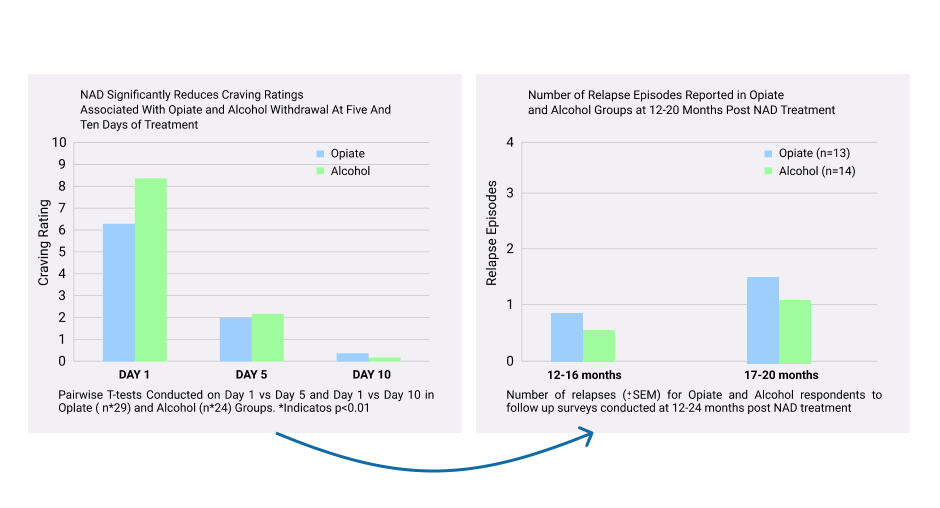
NAD+ IV therapy has been shown to help substance-addicted patients who want to recover in several important ways, compared to conventional recovery treatments.
When administered by IV infusion, NAD+:
- Radically reduces cravings and other physical symptoms of withdrawal
- Reduces stress, depression and anxiety
- Shortens recovery time
- Has no potential for abuse, like some treatment medications
- Boosts energy and improves mood
The San Diego NAD Treatment Center agrees that NAD+ therapy for addiction is best delivered by IV infusion, and not by oral supplements. NAD+ IV therapy is most effective and works more quickly when IV contents are supplemented with a specific amino acid complex and other nutrients.
Follow this link to learn more about NAD+ IV therapy for recovery from Substance Abuse: NAD+ is a Powerful Tool for Combating Substance Addiction.
NAD+ and Physical Performance
For athletes and other physically active adults, one of the harsh realities of life is a decline in physical performance as we age. While a handful of elite athletes may remain competitive into their 40s, most accept the fact that their days of victory over younger opponents are numbered.
In a recent study (Martens et al. 2018) — on humans this time — researchers studied 30 lean, healthy middle-aged and older men and women, aged 55 to 79. The experimental group was given an NAD+ precursor supplement, nicotinamide riboside (NR), while the control group received a placebo. The two groups were matched for age, sex and clinical characteristics. At the end of six weeks, researchers found that NAD+ levels were elevated in the experimental group, and that NAD+ supplementation showed promise for lowering blood pressure and reducing arterial stiffness, both risk factors for heart disease.
Another study (Das et al. 2018) looked at changes in the endothelial cells that line the blood vessels. They noted that aging reduces capillary density and diminishes blood flow to tissues throughout the body, including muscles and vital organs. The experiment revealed that NAD+ therapy improved blood flow and increased endurance in elderly mice. They concluded that NAD+ therapy shows promise for improving blood flow and increasing performance and mobility in older adults.
Regularly boosting your NAD+ levels at the earliest signs of physical decline could be a game-changer for how you age, and could profoundly affect your overall quality of life.
NAD+ IV Therapy in NYC – Where you can get NAD+ Treatment
Getting enough of the precursors that boost NAD+ levels can be a challenge. Certain foods can help, but even a healthy diet cannot provide enough NAD+ to offset its natural decline. Oral supplements also fall short, since they depend on the digestive system for absorption. Pills are often poorly absorbed in the digestive tract, and they may even pass right through your system without ever being broken down.
NAD+ IV therapy provides the most efficient way to boost NAD+. During your NAD+ IV session, vital ingredients are infused directly into your bloodstream and quickly delivered to cells throughout your body. IV therapy completely bypasses your digestive tract, ensuring that every drop can get to work within minutes.
Whether you want to put the brakes on aging, improve your mental and physical performance or treat a serious health condition, NAD+ IV therapy is just around the corner in NYC.
Schedule your NAD+ IV therapy session at Contact Advanced Cryo NYC today and enjoy the benefits of good health for years to come.
Resources:
Das, Abhirup, et al. “Impairment of an endothelial NAD+-H2S signaling network is a reversible cause of vascular aging.” Cell 173.1 (2018): 74-89. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29570999 Hou, Yujun, et al. “NAD+ supplementation normalizes key Alzheimer’s features and DNA damage responses in a new AD mouse model with introduced DNA repair deficiency.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 115.8 (2018): E1876-E1885. Martens, Christopher R., et al. “Chronic nicotinamide riboside supplementation is well-tolerated and elevates NAD+ in healthy middle-aged and older adults.” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29599478 Nature communications 9.1 (2018): 1286. Tarragó, Mariana G., et al. “A potent and specific CD38 inhibitor ameliorates age-related metabolic dysfunction by reversing tissue NAD+ decline.” Cell metabolism 27.5 (2018): 1081-1095. Tullius, Stefan G., et al. “NAD+ protects against EAE by regulating CD4+ T-cell differentiation.” Nature communications 5 (2014): 5101.