
Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative condition affecting one to two percent of the population, for which there is no known cure. Early symptoms are mild and often go undetected until the disease progresses, at which point management of symptoms becomes the primary standard of care.
Advanced symptoms of Parkinson’s and the rate of degeneration vary from one individual to the next, with some people living with mild symptoms for decades, while others make a rapid descent into full disability over the course of several months that terminates in death.
No one knows what causes the onset of Parkinson’s disease, but environmental factors are thought to be a contributing factor. New research is exploring the role of nutrients like NAD and glutathione for Parkinson’s disease symptoms management.
Overview of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s is a neurodegenerative movement disorder whose symptoms progressively worsen over time. A broad spectrum of drugs have been developed to treat Parkinson’s symptoms, with dismal success rates.
Parkinson’s affects the central nervous system, causing cellular damage in the brain that leads to a severe drop in dopamine levels. Dopamine is an important chemical neurotransmitter that helps to deliver messages between the brain and the body, governing movement.
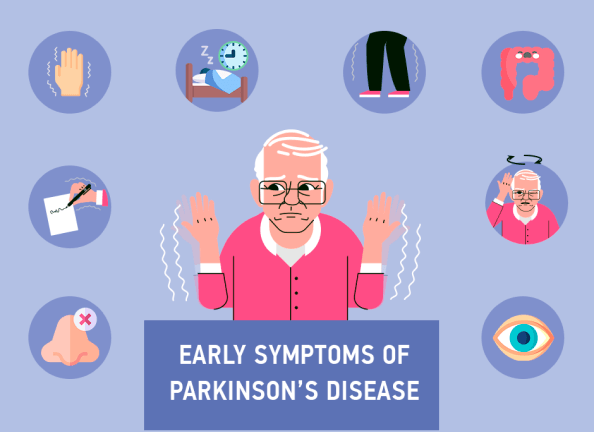
Early symptoms of Parkinson’s disease include:
- A slight tremor in one hand
- Shrinking handwriting
- Reduced sense of smell
- Sleep disrupted with night terrors and violent thrashing
- Reduced balance
- Stiffness when moving or walking
- Chronic constipation
- Mask” of Parkinson’s marked by staring and loss of emotional facial expression
As the disease advances, symptoms become increasingly severe and unmanageable, and loved ones are often faced with difficult decisions for long-term care.
Advanced symptoms of Parkinson’s disease include:
- Uncontrollable shaking and tremors
- Reduced ability to chew and swallow
- Difficulty enunciating words
- Impaired ambulation and frequent falls
- Bent-over posture
- rinary and fecal incontinence
- nability to perform activities of daily living (ADL) like dressing, bathing, and eating
As Parkinson’s approaches its end game, palliative care and hospice with pain management are the final treatment approaches.
Statistics About Parkinson’s Disease
Consider these statistics from the Parkinson’s Foundation:
- Parkinson’s disease is a predominant movement disorder in the USA, with total cases exceeding those of multiple sclerosis, muscular dystrophy and Lou Gehrig’s disease, combined.
- Parkinson’s cases are expected to exceed 1.2 million by 2030.
- About 60,000 new cases are diagnosed in the USA each year.
- Four percent of Parkinson’s patients are diagnosed before age 50.
- Men are one-and-a-half times more likely to be diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease.
How Important is Glutathione for Parkinson’s Treatment?
Glutathione is an antioxidant molecule made up of three amino acids: glutamine, glycine, and cysteine. Your body manufactures glutathione from dietary nutrients, but if your diet is nutrient-deficient, your glutathione levels may be low. Other factors that may lower your glutathione levels are environmental toxins and stress. Glutathione levels naturally decline as you age.
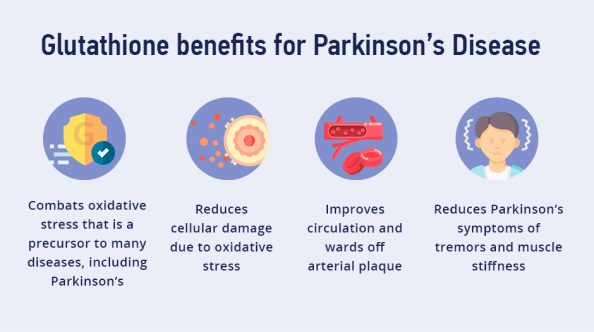
Glutathione benefits for Parkinson’s Disease:
- Combats oxidative stress that is a precursor to many diseases, including Parkinson’s
- Reduces cellular damage due to oxidative stress
- Improves circulation and wards off arterial plaque
- Reduces Parkinson’s symptoms of tremors and muscle stiffness
Neuro-oxidative stress plays a major role in the progression of Parkinson’s disease. Reduced glutathione metabolism can lead to oxidative stress associated with mitochondrial dysfunction, neuroinflammatory response and the neurodegenerative progression of Parkinson’s disease.
Glutathione IV therapy provides neuroprotective and anti-neuroinflammatory agents that appear to reduce the severity of Parkinson’s symptoms and help to slow its progression.
NAD Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease
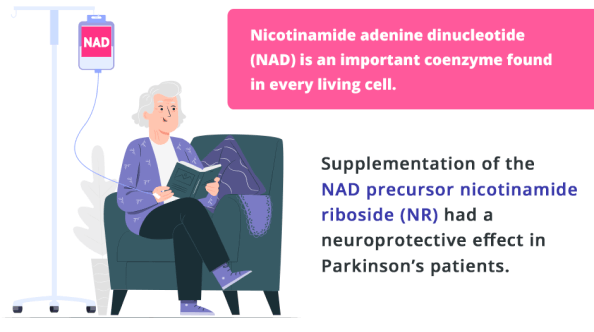
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is an important coenzyme found in every living cell. It supports multiple functions in human metabolism, including cellular metabolism in the brain. NAD levels decline with age, and NAD deficiency has been linked to many diseases of old age, including Parkinson’s disease.
New research shows a correlation between an increase in brain cellular NAD levels and improvement of symptoms in Parkinson’s patients. The study found that supplementation of the NAD precursor nicotinamide riboside (NR) had a neuroprotective effect in Parkinson’s patients.
Treating Parkinson’s Symptoms with IV Therapy
In the advanced stages of Parkinson’s disease, patients have a hard time chewing, swallowing and digesting food. As a consequence, they often become nutritionally deficient.
Supplements in the form of pills and capsules can be difficult to swallow, and there is no guarantee that they will be broken down and absorbed in the digestive process, which is also impaired in Parkinson’s patients.
Intravenous infusion provides a safe and effective alternative for delivering NAD and glutathione to Parkinson’s patients. Because they are nutrients and not drugs, no prescription is needed, and there are no negative side effects.
Family members and caregivers often try the full gamut of Parkinson’s medications without success in alleviating the symptoms of Parkinson’s or slowing its progression. Nutrient IV therapy offers an evidence-based natural alternative to drugs, without their many negative side effects.
NAD IV Therapy and IV Glutathione Therapy for Parkinson’s in NYC
If you or your loved one is suffering from Parkinson’s disease, nutrient IV therapy may offer an all-natural solution to alleviate symptoms and slow the progression of Parkinson’s disease. InVita Wellness offers NAD and glutathione IV therapy in our clinic on Broadway. Contact InVita Wellness today, and get the nutritional support you need to manage Parkinson’s disease and slow its progression.