
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder that causes painful swelling of the joints and deterioration of joint cartilage. The exact cause of RA is currently unknown, and available pharmacological treatments are relatively ineffective in managing symptoms or in halting the progression of RA. However, new research on NAD+ for rheumatoid arthritis therapy offers new hope for sufferers of RA.
Onset of RA
Rheumatoid arthritis is a degenerative inflammatory disorder that falls under the umbrella of autoimmune disease, where your own immune system attacks apparently healthy cells. In RA, T-cells attack the synovium, the joint lining that produces synovial fluid to lubricate the joints. As RA progresses, the synovial membrane becomes inflamed and thickened, causing the joint to become tender and painful.
While RA can occur at any age, it predominantly appears in middle age, and is more common in women than in men. According to the Arthritis Foundation, the average age range for RA onset in women is 30-60 years. Men rarely develop RA under the age of 45, and women are three times more likely to develop RA than men.
RA Symptoms
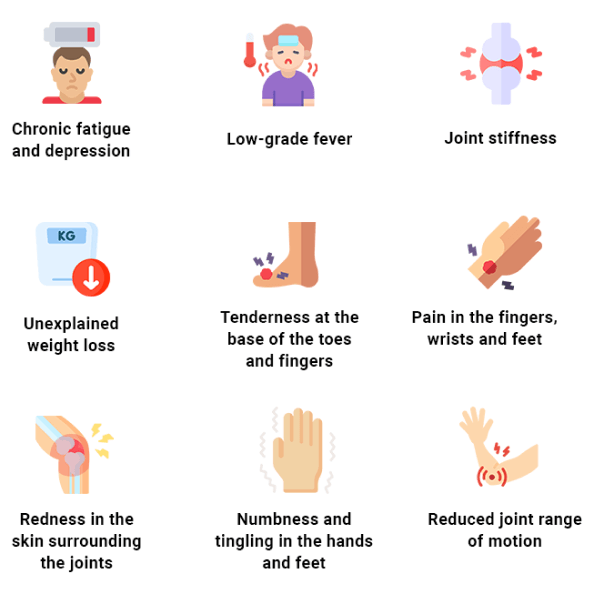
Symptoms typically appear simultaneously in joints on both sides of the body. Early symptoms of RA include:
- Chronic fatigue and depression
- Low-grade fever
- Joint stiffness, especially after bouts of inactivity
- Unexplained weight loss
- Tenderness at the base of the toes and fingers
- Pain in the fingers, wrists and feet
- Redness in the skin surrounding the joints
- Numbness and tingling in the hands and feet
- Reduced joint range of motion
As RA advances, it can cause deterioration of the joint cartilage and nearby bone tissue. The joints may become deformed, and hard nodules may appear around the joints. RA-associated inflammation can also affect the eyes, skin, blood vessels, lungs and heart.
Risk Factors of RA
While it is unclear what causes the autoimmune response that triggers the onset of RA, certain risk factors have been identified.
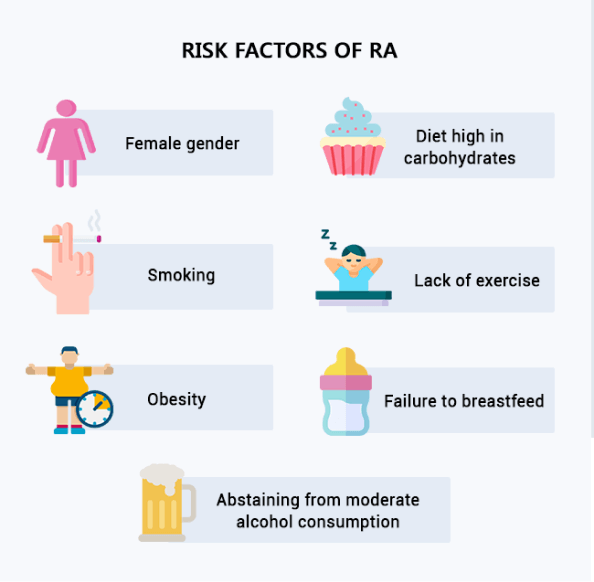
Known risk factors for RA include:
- Female gender
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Diet high in carbohydrates
- Lack of exercise
- Failure to breastfeed
- Abstaining from moderate alcohol consumption
NAD+ and RA Progression
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is a coenzyme that plays an important role in cellular respiration within the cells’ mitochondria. Mitochondria are tiny organelles found in every cell, where oxygen is used to convert carbs and fats to ATP, the energy molecule.
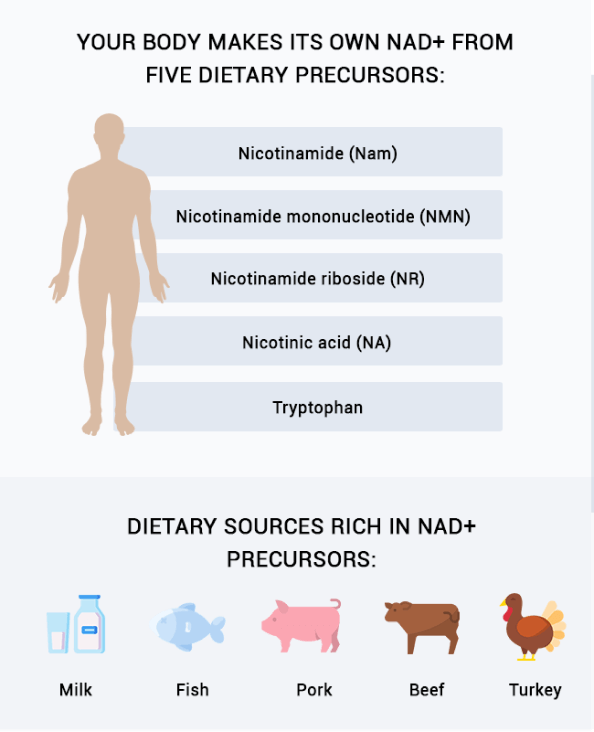
Your body makes its own NAD+ from five dietary precursors:
- Nicotinamide (Nam)
- Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN)
- Nicotinamide riboside (NR)
- Nicotinic acid (NA)
- Tryptophan
Patients with RA tend to have low levels of NAD+ precursors. Dietary sources rich in NAD+ precursors include:
- milk
- fish
- pork
- beef
- turkey
Production of NAD+ diminishes with age, especially in sedentary individuals with nutrient deficiencies. Regular exercise and a nutrient dense diet promote NAD+ production and the growth of cellular mitochondria, which may in turn reverse inflammation and reduce RA symptoms.
In addition, research shows that a low carb ketogenic diet may have a profound effect in reducing RA inflammation, while at the same time promoting healthy body weight.
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Scientific NAD+ Research
NAD+ has recently attracted the attention of scientists looking to unlock the underlying causes of aging and age-related diseases. Multiple studies have emerged that link low NAD+ levels to the progression of rheumatoid arthritis.
- A 2018 review of related studies illuminates the role of NAD+ related enzymes in the onset and progression of RA, and explores the potential of NAD+ supplementation as a therapeutic treatment for RA.
- A 2021 study explores the potential of NAD+ boosters to reduce the oxidative, apoptotic and inflammatory profiles of RA, and concludes that supplemental NAD+ boosters may provide an effective therapeutic treatment for RA.
- Another study finds that fasting is effective in reducing the symptoms of RA, and explores the potential of a ketogenic diet for reducing RA inflammation and slowing its progression.
There is no doubt that the relationship between low NAD+ levels and the onset and progression of RA will continue to pique the curiosity of scientists seeking a solution for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, and we can expect to see more research in the future that links NAD+ to autoimmune disorders like RA.
Rheumatoid Arthritis NAD+ Treatment in NYC
your quality of life. NAD+ IV therapy provides an all-natural solution for boosting your NAD+ levels, to fight inflammation and slow the progression of RA.
You can get NAD+ treatment in NYC at InVita Wellness on Broadway.
Because NAD+ is a nutrient and not a drug, NAD+ IV therapy has no negative side effects, and you don’t need a prescription. Contact InVita Wellness today, and boost your NAD+ levels to stop RA in its tracks.
Resources
Chen, Weiqian, Caihong Yi, and Lin Jin. “The role of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: potential implications for treatment.” EMJ 3.3 (2018): 90-97.
Ciaffi, Jacopo, et al. “The Effect of Ketogenic Diet on Inflammatory Arthritis and Cardiovascular Health in Rheumatic Conditions: A Mini Review.” Frontiers in Medicine 8 (2021).
Perez-Sanchez, C., et al. “POS0394 NAD+ boosters reestablish the altered NAD+ metabolism of leukocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients improving their oxidatie, apoptotic and inflammatory status.”(2021): 426-426.