Vitamin B3, also known as niacin, is an important water soluble vitamin that is essential for human health. Water soluble vitamins cannot be stored in your body, and any extra that your cells cannot use gets flushed out, meaning you have to replenish them on a regular basis. Niacin deficiency is responsible for a disease called pellagra that affects the skin, as well as the digestive and nervous systems. If left untreated, B3 deficiency can lead to death.
NAD+ Benefits
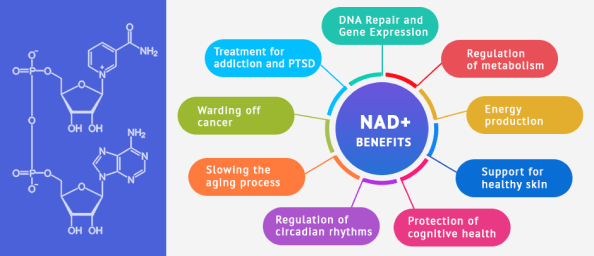
Vitamin B3 is made up of nicotinic acid, nicotinamide and nicotinamide riboside, which are precursors to the coenzyme NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide). The amino acid tryptophan is also an NAD+ precursor. Mounting research points to NAD+ as a critical nutrient for multiple essential body functions.
NAD+ plays an important role in many facets of human health, including:
- DNA Repair and Gene Expression: NAD+ is the only substrate your body can use to make sirtuins and PARP enzymes necessary for DNA repair, making it essential for genome stability.
- Regulation of metabolism: Metabolism is the sum of chemical processes that occur in your body to keep you alive. NAD+ mediates redox (oxidation reduction) reactions, carrying electrons between NAD+ and NADH to maintain healthy metabolism.
- Energy production: NAD+ plays an essential role in mitochondrial health. Mitochondria are tiny organelles found within cells that use oxygen, glucose and fat to produce ATP, the energy molecule. ATP in muscle cells enables repeated muscle contraction during exercise.
- Support for healthy skin: NAD+ supports skin health by strengthening the epidermal barrier, improving skin quality by preventing infections, water loss and wrinkles.
- Protection of cognitive health: NAD+ protects your brain from damaging oxidative stress that can impair focus and memory, and contribute to neurodegenerative disorders.
- Regulation of circadian rhythms: Circadian rhythms dictate your sleep-wake cycle. NAD helps to regulate circadian rhythms so you get adequate sleep.
- Slowing the aging process: Your body naturally decreases its production of NAD+ as you get older. Lower NAD+ levels reduce DNA repair and have been associated with cognitive decline and metabolic disease in older adults.
- Warding off cancer: Several studies suggest that NAD+ may play a role in cancer prevention. In a recent trial using high-risk subjects, a daily dose of nicotinamide reduced the rate of premalignant skin lesions and nonmelanoma cancers. Cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy are especially susceptible to NAD+ deficiency.
- Treatment for addiction and PTSD: NAD+ is effective in reducing drug cravings in recovering addicts, and has been found to suppress PTSD symptoms.
How to Replenish Vitamin B3
It is fairly easy to find dietary sources of niacin. B3 is found in many common foods, including beef, fish and poultry, legumes and peanuts, and in fortified cereals. However, as you age, your body is less able to convert B3 to NAD+. Even with a niacin-rich diet, you may not be able to protect yourself from DNA damage and physical decline associated with aging.
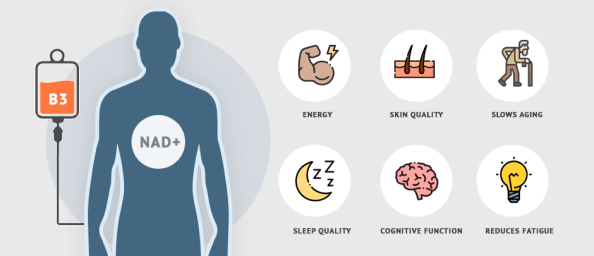
A safe and effective way to boost NAD+ levels is via IV infusion therapy. Rather than waiting for food to be broken down in your digestive tract and nutrients to be absorbed, IV infusion delivers a potent dose of NAD+ precursors directly to your blood stream, where they are quickly delivered to depleted cells throughout your body.
Regular NAD+ therapy can improve your health in many ways:
- reduces fatigue
- increases energy
- improves skin quality
- slows aging
- improves cognitive function
- enhances sleep quality
NAD+ Treatment in NYC

Advanced Cryo NYC offers a large selection of IV nutrient cocktails, injection therapies, cryotherapy and more, to improve your health and enhance your beauty. Contact our clinic today to schedule your NAD+ IV therapy session, or to learn more about our other health and beauty services.
Resources:
Stein, Liana Roberts, and Shin-ichiro Imai. “The dynamic regulation of NAD metabolism in mitochondria.” Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism 23.9 (2012): 420-428.
Yaku, Keisuke, et al. “Metabolism and biochemical properties of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) analogs, nicotinamide guanine dinucleotide (NGD) and nicotinamide hypoxanthine dinucleotide (NHD).” Scientific reports 9.1 (2019): 1-12.