
Dementia is an umbrella term for gradual cognitive decline, marked by loss of memory, impaired speech, reduced capacity for problem-solving, and other mental impairments. It is estimated that upwards of 10 percent of adults over age 70 in the United States have some form of dementia.
In looking for common denominators in dementia patients, scientists have found that dehydration is almost ubiquitous. Learn how dehydration affects cognition, and how IV hydration therapy can help protect and restore cognitive function in older adults.
Dehydration and the Elderly
Besides oxygen, water is the most essential element for sustaining life, yet many adults in Western societies are chronically dehydrated. A healthy human body is made up of two-thirds to three-quarters water, depending on lean muscle mass, and the human brain is 80 percent water.
Good hydration is vital to the function of every system in your body. When you are chronically dehydrated, your body is forced to compensate in ways that can have long-term health effects.
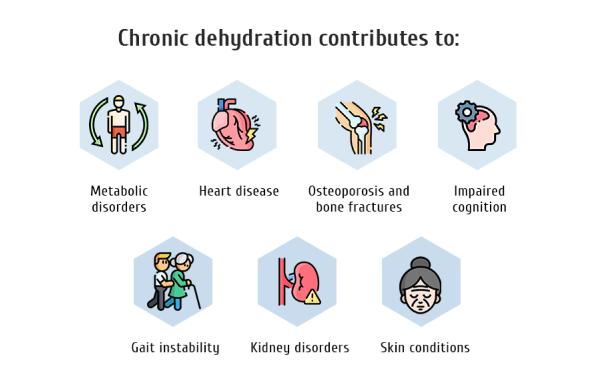
Chronic dehydration contributes to:
- Metabolic disorders
- Heart disease
- Osteoporosis and bone fractures
- Impaired cognition
- Gait instability
- Kidney disorders
- Skin conditions
Dehydration is rampant among older adults. According to one scientific resource, as many as 17-28 percent of older adults are chronically dehydrated, and dehydration is one of the most common causes of hospitalization in older adults.
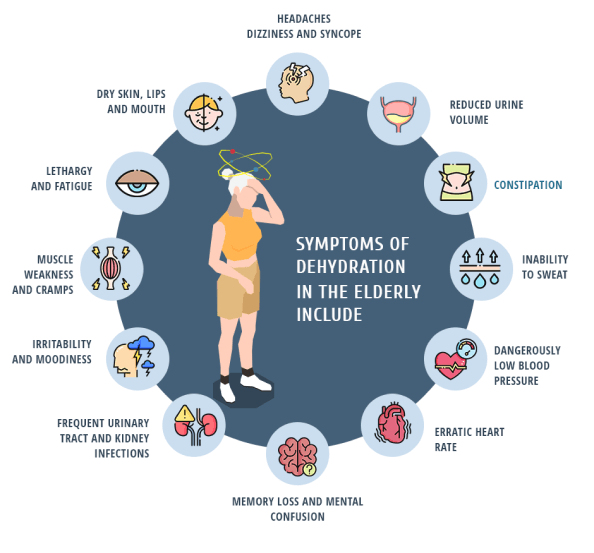
Symptoms of dehydration in the elderly include:
- Muscle weakness and cramps
- Lethargy and fatigue
- Dry skin, lips and mouth
- Headaches
- Dizziness and syncope
- Reduced urine volume
- Constipation
- Inability to sweat
- Dangerously low blood pressure
- Erratic heart rate
- Memory loss and mental confusion
- Irritability and moodiness
- Frequent urinary tract and kidney infections
Because many of the symptoms of dehydration are shared with many other health conditions, patients may be misdiagnosed and mistreated with medications, when all they really need is water.
Causes of Older Adult Dehydration
Failure to drink enough water is the primary underlying cause of dehydration in general. Instead of water, many people choose sugary soft drinks, caffeinated beverages, and alcohol.
In addition, older adults tend to eat fewer fresh fruits and vegetables, which are key sources of dietary fluids. Dental issues, digestive problems and poor access may be contributing factors. Many opt for high-sodium, high-sugar processed foods that are easier to chew and digest.
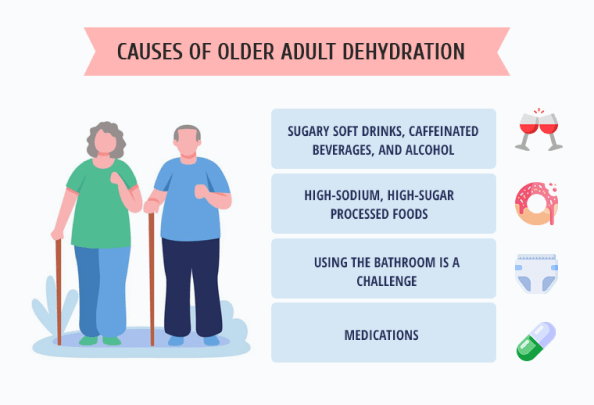
For many older adults, using the bathroom is a challenge. Making it to the bathroom on time, undressing, getting on and off the toilet, and hygiene are all issues that cause some elderly people to restrict their fluid intake. Older people who wear adult diapers may be embarrassed about wetting themselves, and they may limit their fluid intake to preserve their dignity and not be a nuisance to caregivers.
Medications may also play a significant role. Many medications prescribed for metabolic disorders have a diuretic effect that reduces body fluid levels and contributes to dehydration. In some instances, dehydration may be the underlying cause of metabolic disorders, and the drugs to treat them worsen the situation, creating a vicious cycle that undermines the patient’s health.
Dehydration and Brain Health
Dehydration can have a profound effect on brain function. A loss of as little as 1-2% of total body water has been shown to diminish cognitive performance in the elderly.
Cognitive abilities impacted by dehydration include:
- Short-term memory
- Problem-solving
- Attention and focus
- Speech
- Articulation of thoughts
- Mental clarity
In the long run, impaired cognition can lead to loss of independence and reduced overall quality of life. Families of older adults with dementia are burdened with long-term care decisions, and suffer emotional distress as the vitality of their loved ones fades away before their eyes.
Benefits of IV Hydration Therapy for Older Adults
Drinking enough water on a daily basis can be challenging for older adults, especially if they have reduced mobility. Also, getting the right balance of fluids and electrolytes is crucial for a healthy heart, brain and central nervous system. Dry heat during the winter and hot humid weather in the summer both contribute to dehydration.
Weekly IV hydration therapy can help ensure that your brain and body are getting all fluids and electrolytes they need to function at their best. During an IV therapy session, you simply relax for about an hour as your IV hydration cocktail is infused directly into your bloodstream.
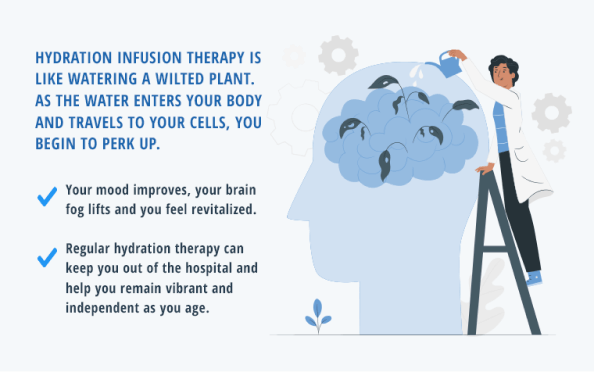
Hydration infusion therapy is like watering a wilted plant. As the water enters your body and travels to your cells, you begin to perk up. Your mood improves, your brain fog lifts and you feel revitalized. Regular hydration therapy can keep you out of the hospital and help you remain vibrant and independent as you age.
Hydration IV Therapy in NYC
Staying hydrated is fundamental to human health, especially for the elderly, and hot and humid days in NYC can be brutal for older adults. Water alone is not enough to stay fully hydrated. You need electrolytes for nerve impulse conduction, to keep your heart beating and your systems running smoothly.
Regular IV hydration therapy sessions help ensure that your body gets all the fluids and electrolytes you need for physical and mental health. Contact InVita Wellness today for IV hydration in NYC, and see what a difference good hydration can make for your health, longevity and quality of life.
Resources:
Edmonds, Caroline J., et al. “Dehydration in older people: A systematic review of the effects of dehydration on health outcomes, healthcare costs and cognitive performance.” Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics 95 (2021): 104380.
Masento, Natalie A., et al. “Effects of hydration status on cognitive performance and mood.” British Journal of Nutrition 111.10 (2014): 1841-1852.