Chronic inflammation is on the rise due to today’s stressful lifestyles, poor nutrition, dehydration, and lack of quality sleep. Inflammation often goes hand-in-hand with other conditions like heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, and obesity. This cluster of diseases is known as Metabolic Syndrome, and the National Institute of Health estimates that 1 in 3 adults suffer from it.
People with metabolic syndrome want to to get rid of inflammation fast, but it is actually a normal defense mechanism of your immune system in response to injuries or pathogens. In a way, cytokines and inflammatory cells are your body’s first responders, sent throughout your body to shut down pathogens and facilitate the healing process.
Unfortunately, conditions like Metabolic Syndrome can cause too much inflammation where it is not needed. The presence of excess inflammatory cells can do more harm than good, damaging the body’s tissues as the problem persists for months or years.
What You Should Know about Nutrient IV Therapy
Luckily, if you’re looking for a fast way to reduce inflammation, anti-inflammatory IV (intravenous) nutrients can help. One of the primary benefits of IV therapy is the lightning-fast delivery of essential nutrients directly to the body’s cells.
Normally, when you eat food or orally ingest a nutrient supplement, your digestive system has to break them down to be processed by the liver before they are released into your bloodstream. With IV therapy, the digestive system is bypassed, and nutrients are quickly delivered to your cells to provide much faster relief from inflammation.
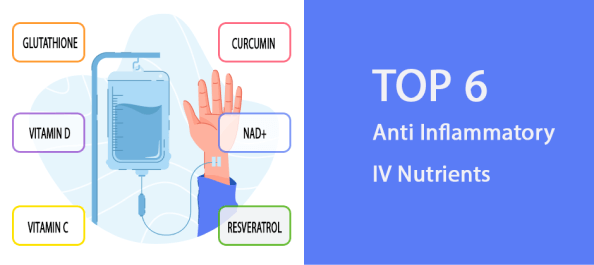
Learn about six potent IV nutrients that are top-rated anti-inflammatory supplements.
Glutathione
Glutathione is a top anti-inflammatory supplement that is naturally produced in the body in large quantities. It is the most abundant antioxidant in the body and has the power to fight multiple diseases and reverse signs of aging.
Antioxidants play a major role in the prevention of a host of diseases like cancer and heart disease, since they help to protect the cells from unstable atoms known as free radicals – molecules that contain oxygen with an uneven number of electrons. This causes them to react easily with other molecules, resulting in significant chain chemical reactions.
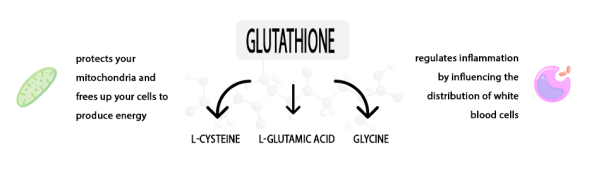
Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance of antioxidants and free radicals, which is a significant contributor to inflammation. Glutathione is a tripeptide containing three amino acids: L-cysteine, L-glutamic acid, and glycine. It is a detoxifying agent that protects your mitochondria and frees up your cells to produce energy. It also regulates inflammation by influencing the distribution of white blood cells.
Vitamin D
People who suffer from chronic inflammation often wonder what to take for inflammation in the body. One of the most accessible options is Vitamin D, which your body manufactures when exposed to natural sunlight. Hormonal Vitamin D has been shown to slow the production of inflammatory cytokines like interleukin-12, according to a study by the Boston University School of Medicine.
More evidence is emerging that suggests that Vitamin D can play a role in reducing the risk of autoimmune illnesses like multiple sclerosis and type 1 diabetes, along with other inflammatory illnesses, including cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
For patients suffering from the effects of chronic inflammation and metabolic disorders, research has shown that Vitamin D reduces their severity.
Vitamin C

According to the National Center for Biotechnology Information, Vitamin C has the ability to reduce inflammation by lowering levels of hs-CRP, IL-6, and FBG in people with high blood pressure, diabetes, and obesity. Vitamin C is known as a powerhouse for immunity. Since inflammation is an overreaction of the immune system in chronic illnesses, Vitamin C can be a frontline defense against it.
Patients who suffer from acute respiratory illnesses like COVID-19, pneumonia, and the flu are often given high-dose Vitamin C via IV as a key way to reduce inflammation. Vitamin C is often recommended for the prevention of colds and flu. It is plentiful in green, red, orange, and yellow fruits and vegetables, and a diet rich in these can help to prevent illness over the long-term.
Curcumin
Turmeric is one of the strongest anti-inflammatory herbs. If you’re a fan of Indian or Caribbean curry dishes, this vibrant yellow spice may be one of your favorites. It contains the compound curcumin, which has been shown to reduce the symptoms of arthritis, cancer, heart disease, and inflammatory bowel disease.
According to the National Institutes of Health, curcumin helps to reduce inflammation by regulating inflammatory signaling pathways, and by inhibiting the production of inflammatory mediators.
Curcumin is a fat-soluble nutrient, so it can be advantageous to use turmeric with meals that are high in fat. When used alone, curcumin is known for being poorly absorbed into the bloodstream. Combining curcumin with other herbs can help to optimize its effects. For example, black pepper contains a substance called piperine which can boost curcumin’s absorption rate and make your meal even tastier!
Resveratrol
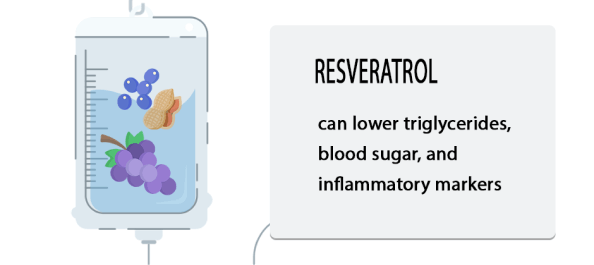
Resveratrol is another powerful antioxidant found in purple-colored fruits like blueberries and grapes. You can also get a healthy dose of it from peanuts, dark chocolate, and red wine. It can lower triglycerides, blood sugar, and inflammatory markers. If you suffer from obesity, ulcerative colitis, liver disease, and many of the aforementioned inflammatory ailments, resveratrol can help to relieve your symptoms and reduce their effects.
Resveratrol is included in the category of plant micronutrients known as polyphenols and is originally produced within plant cells to help them survive environmental stresses like disease and drought. It is yet another weapon in the fight against free radicals. In studies involving patients whose obesity and inactivity resulted in low-grade inflammation, resveratrol was proven to be a great go-to supplement for its reduction.
NAD+
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) is a co-enzyme that helps to jumpstart the functions of many other enzymes throughout the body. It is derived from niacin and is also known as vitamin B3. It helps to regulate immune function and, therefore, has a direct influence on the inflammatory response.
NAD is naturally produced in the body’s cells and can also be found in niacin-rich foods like grains, meats, and milk. However, stress, smoking, poor diet, and lack of sleep are among the environmental factors that can prevent your cells from producing enough of this substance.
According to the Society for Endocrinology, exercise can significantly increase NAD levels within the body. This is promising, particularly for people who suffer from arthritis, and helps to explain why the right forms of moderate exercise result in decreased joint pain.

Cryotherapy
If you’ve ever gone for a nice long run or finished up a weight-training session and realized you pulled a muscle, you know applying ice can be a lifesaver. Bodybuilders, athletes, and fitness enthusiasts often look for ways to reduce inflammation, and cryotherapy is increasing in popularity as a solution.
While studies are still being conducted for a fuller understanding of its effectiveness, cryotherapy does reduce the body’s inflammatory response and promotes the regeneration and repair of muscle tissue, post-exercise.
Thanks to new technology, you can get fast and effective cryotherapy benefits by using a cryo chamber for whole body cryotherapy, or via local cryotherapy that targets specific inflamed tissues.
Get Safe and Effective Anti-Inflammatory IV Therapy in NYC
A consistently healthy diet rich in nutrient-dense foods, along with adequate sleep and regular exercise, can help to eliminate inflammation over the long-term. But if you’re looking for a fast way to reduce inflammation, try fast-acting anti-inflammatory IV therapy at InVita Wellness.
Enjoy a relaxing IV therapy session in our ultra-modern, spa-like facility. Your session may last between one hour and 90 minutes, so bring your phone, your laptop or a book, or just plan to take a refreshing power nap. Contact InVita Wellness today, and fight inflammation from the inside-out with anti-inflammatory IV therapy.
Sources:
https://medschool.vanderbilt.edu/vanderbilt-medicine/the-good-the-bad-and-the-ugly-of-inflammation/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7402141/
https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/multimedia/antioxidants/sls-20076428
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/
https://www.purdue.edu/newsroom/releases/2021/Q4/researchers-study-the-link-between-vitamin-d-and-inflammation.html
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/vitamin-d-supplements-may-help-reduce-chronic-inflammation-study-finds
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4492638/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8572027/
https://reader.elsevier.com/reader/sd/pii/S0925443915000071
https://www.endocrinology.org/endocrinologist/135-spring20/features/nutrition-nad-and-exercise-vitamin-b3-supplements-to-stay-fit-and-healthy
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4698758/
Links:1.
https://www.niehs.nih.gov/health/topics/conditions/inflammation/index.cfm
“Inflammation”, National Institute of Health, April 28, 20212.
2.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925443915000071
Poulsen, M., et. al., “Resveratrol and inflammation: Challenges in translating pre-clinical findings to improved patient outcomes”, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) – Molecular Basis of Disease, Volume 1852, Issue 6, June 2015, Pages 1124-1136.